README
Event visualizer
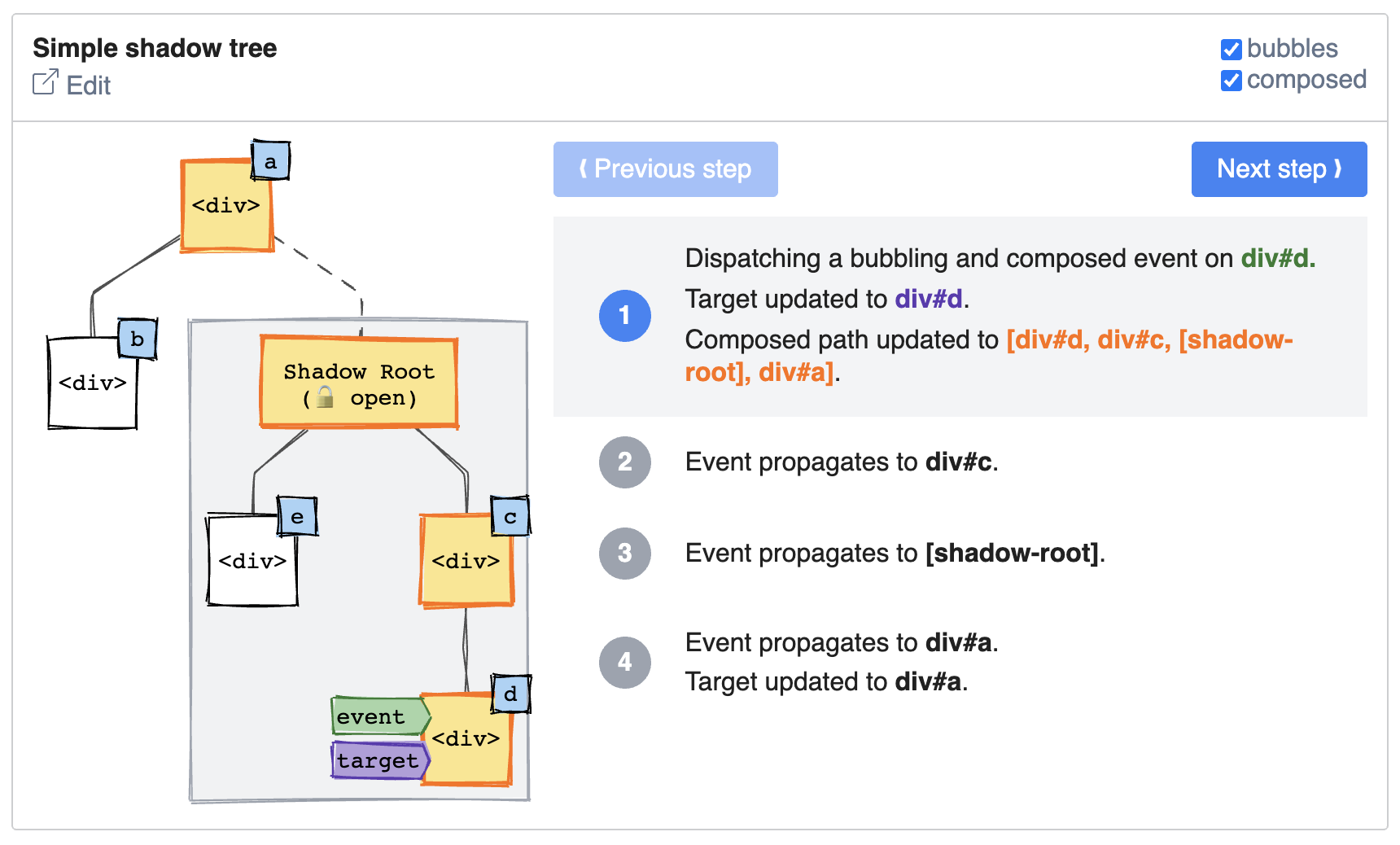
A visualization tool to better understand how events propagate in the shadow DOM.
Overview
The way DOM events propagate in the shadow DOM is not intuitive for developers onboarding with web components. Event configuration, DOM structure and closed vs. opened shadow trees are many factors influencing event propagation.
This project is an attempt to bring clarity to this subject by offering a visual playground explaining how events propagates step-by-step in the shadow DOM.
Try it out: Demo / Playground
Installation
This package can be consumed as an NPM package.
$ npm install --save @pmdartus/event-visualizer
Alternatively for drop-in consumption this package can directly be loaded from Skypack CDN.
<script type="module" src="https://cdn.skypack.dev/@pmdartus/event-visualizer"></script>
<event-visualizer>
Properties / Attributes
| Property | Attribute | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
label |
label |
string |
"Event propagation" |
The label name. |
eventBubbles |
event-bubbles |
boolean |
false |
Indicates wether the dispatched event should bubbles or not. |
eventComposed |
event-composed |
boolean |
false |
Indicates wether the dispatched event should be composed or not. |
Slots
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| default | Accepts a single <template> element representing the DOM tree to visualize. Refer to the DOM tree definition section for more details. |
DOM tree definition
The visualized DOM tree is configured by passing a <template> element in the default slot. The content of the template tag is interpreted by the <event-visualizer> custom element to render the visual previous of the DOM tree and emulate event dispatching:
- Shadow trees can be defined directly in HTML via the declarative shadow DOM syntax with the difference difference that the
shadow-rootattribute is renamed todata-shadow-root. - The original event target is defined by adding a
targetattribute. - A label can be added to any element using the
idattribute. - Restrictions:
- The template content should have root element.
- The DOM should have a one element with the
targetattribute.
<event-visualizer label="Simple tree">
<template>
<div id="a">
<div id="b" target></div>
</div>
</template>
</event-visualizer>
<event-visualizer label="Simple shadow tree">
<template>
<div id="a">
<template data-shadowroot="open">
<div id="b" target></div>
</template>
<div id="c">
</div>
</template>
</event-visualizer>