README
Web3 Events
Library for robust handling of web3 events listening and basic blockchain reorganisations.
Table of Contents
Usage
import { Web3Events, Contract } from 'web3-events'
import { Eth } from 'web3-eth'
import Sequelize from 'sequelize'
const sequelize = new Sequelize(...) // Defined in your application
const eth = new Eth('provider')
await Web3Events.init(sequelize)
const events = new Web3Events(eth, {store: {}})
const coolContract = new Contract(abi, '0x123', 'coolContract')
type SomeEvent = { returnValues: {data: string} }
const eventsEmitter = events.createEventsEmitter<SomeEvent>(coolContract, { events: ['SomeEvent'] })
eventsEmitter.on('event', (event: SomeEvent) => {
console.log('We got Some Event with data: ', event.returnValues.data)
})
Components overview
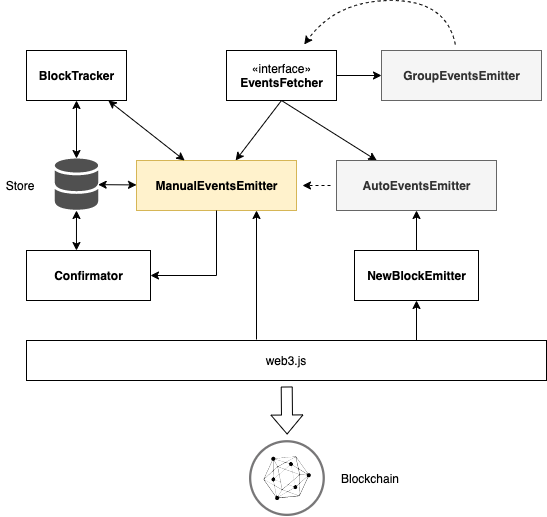
There are several building blocks that cooperate to make the listening on events happen. Bellow is a basic overview:
Web3Events: higher level class that serves as glue for the rest of the components, making easier for users to createEventsEmitters.BlockTracker: component that serves for persistent storage of data regarding what blocks were fetched or processed.NewBlockEmitters: component that tracks whether there is a new block on the blockchain. It serves as a trigger for most of the actions in the others components.Confirmator: component that handles confirmations of blocks based on the configuration.EventsFetcher: the main interface that defines simple API for fetching events. There are three implementations.ManualEventsEmitter: this implementation works only throughfetch()method that you have to call yourself manually.AutoEventsEmitter: this implementation useNewBlockEmitterto automatically triggerfetch()upon new blocked detected and emits them as events.GroupEventsEmitter: this implementation groups already existing Emitters under one Emitter. Mainly used for logical groupping of Contracts or when you need cross-Contract order dependant Events processing.
Confirmations
Blockchain reorganization is a well-known problem that makes development of blockchain's client applications rather hard, because the data can change under your hand. This library tries to tackle this problem with basic approach of supporting confirmations a.k.a waiting configured number of blocks before pronouncing a block valid. The main downside of this approach is that once event is confirmed, then there is nothing to do about it. Choosing the numbers of confirmations is important and it is the eternal struggle between security and user experience. If you will use a lot of confirmations you can be pretty sure that the block won't disapear in blockchain, but in the same time you are keeping your users waiting.
Do your own research about statistics of depth of reorgs (eq. how many blocks becomes orphaned in reorganization) on your blockchain and decide based on your usecase!
Logger support
This library has extensive logging support. By default these log are aggregated by debug package which
has basic logging capability mainly for development stage. If you want to view the logs set environmental variable `DEBUG='web3events*'.
You can pass your own logger for better logging support it just have to adhere to the Logger interface having functions:
debug(), verbose(), info(), warn() and error(). The signature of these functions is: (message: string | object, ...meta: any[]) => void.
Optionally it can have function extend(name: string) => Logger that creates a new Logger with an extended name. E.g. if you have for example
logger web3events calling on it extend('blockTracker') would returned logger with name web3events:blockTracker.
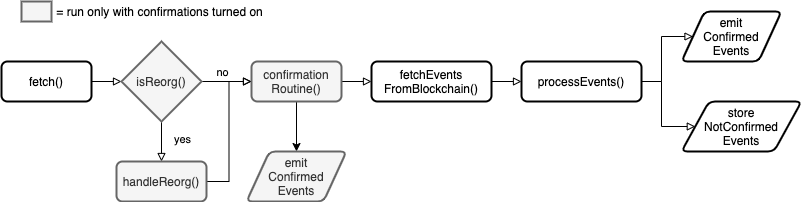
Fetch flow
To better understand what happens when events are fetched from blockchain see bellow flow chart.
API
Web3Events class
Higher level class that serves as glue for the rest of the components. It encapsulate several dependencies that EventsEmitters have like BlockStore, Eth instance and NewBlockEmitter, making easier for users to create EventsEmitters.
constructor(eth, options)
Parameters:
eth(Eth) - instance of web3.js's Eth, that defines the connection to the blockchain.options(Web3EventsOptions|undefined) - several non-mandatory options.options.store(object|undefined) - an object that serves as store whereBlockTrackerstores all metadata about processed and fetched block. It is good idea to use some solution that will make this data persistent across restarts of the application, for examplesequelize-store. If not passed than you have to pass your own instance ofBlockTrackerwhen callingcreateEventsEmitter().options.logger(Logger|undefined) - instance of custom logger as described in Logger support.options.defaultNewBlockEmitter(NewBlockEmitterOptions|NewBlockEmitter|undefined) - eitherNewBlockEmitterinstance or options that should be used to construct defaultNewBlockEmitterthat will be used when no instance is passed to thecreateEventsEmitter().
static init<Events>(sequelize) => Promise<void>
Initialization function which adds our database models to Sequelize instance. Needs to be run prior creating Web3Events instance.
Parameters:
sequelize(Sequelize) - instance of Sequelize
createEventsEmitter<Events>(contract: Contract, options: EventsEmitterCreationOptions) => AutoEventsEmitter<Events>
The main method that creates AutoEventsEmitter class with either provided or default NewBlockEmitter.
Parameters:
contract(Contract) - instance ofContractthat the events will be listened uponoptions(EventsEmitterCreationOptions | undefined) - options that can customize the creation of theAutoEventsEmitteroptions.blockTracker(BlockTracker) - Instance of custom BlockTracker used for the Events Emitteroptions.newBlockEmitter(NewBlockEmitter | NewBlockEmitterOptions) - NewBlockEmitter instance or its options that will be used to create itoptions.logger(Logger) - Custom Logger instanceoptions.serialListeners(boolean) - Defines if the listeners should be processed serially.options.serialProcessing(boolean) - Defines if the events should be kept in order and processed serially.options.autoStart(boolean; default istrue) - Defines if the EventsEmitter should automatically start listening on events when an events listener for events is attached.- for other options see
ManualEventsEmitterOptions
groupEventsEmitters<Events>(eventsEmitters: AutoEventsEmitter<any>[], options: CreateGroupEmitterOptions) => AutoEventsEmitter<Events>
Method that takes several EventsEmitters and group them under one emitter.
The EventsEmitters must not have any newEvents listeners! Nor they can be attached later on!
Except of some logical grouping of Emitters, this is mainly meant for Contracts that have order depending evaluation.
If that is the case use the flag options.orderedProcessing with most probably options.serialProcessing flag.
Parameters:
eventsEmitters(EventsFetcher[]) - array of Emitters that will be grouped.options(CreateGroupEmitterOptions|undefined) - for all options seeCreateGroupEmitterOptions. Bellow is basic listing.options.orderedProcessing(boolean) - defines if the events from emitters ordered using blockNumber, transactionIndex and logIndex to determine order of the events.options.newBlockEmitter(NewBlockEmitter | NewBlockEmitterOptions) Custom instance of NewBlockEmitteroptions.serialListeners(boolean) - Defines if the listeners should be processed serially.options.serialProcessing(boolean) - Defines if the events should be kept in order and processed serially.options.autoStart(boolean; default istrue) - Defines if the EventsEmitter should automatically start listening on events when an events listener for events is attached.
Contract class
A class that extends web3.js's Contract class with some metadata.
contstructor(abi, address, name)
Parameters:
abi(AbiItem[]) - ABI that defines the Contractaddress(string) - an address of the deployed contractname(string) - a name of the Contract used mainly for internal usage and logging
ManualEventsEmitter<Events> class
The main component that performs fetching and processing of Contract's events. **It fetches events from the blockchain
using web3.js's getPastEvents() call, so the blockchain node that you are connecting to have to support eth_getLogs() call! **
This class serves mainly as the basic building blocks for other components, but if you need your own triggering logic then it is a standalone component you can use as you wish.
constructor(eth: Eth, contract: Contract, blockTracker: BlockTracker, baseLogger: Logger, options?: ManualEventsEmitterOptions)
Parameters:
eth(Eth) - Instance of Web3.jsEthclass defining connection to blockchain.contract(Contract) - Instance ofContractclass defining the contract of whose events will this emitter will listen on.blockTracker(BlockTracker) - Instance ofBlockTrackerthat will store information about last fetched and processed blocks.baseLogger(Logger) - Instance ofLoggerthat will be used to log information about fetching and confirming events.options?(ManualEventsEmitterOptions | undefined) - Options specifying behavior of the Emitter:options.topics?(string[] | string[][] | undefined) - Non-hashed topics of the Event's signatures. Has priority overoptions.eventsand at least one has to be specified.options.events?(string[] | undefined) - Name of events that will be listend on. Less performant thenoptions.topics. At least this ortopicshas to be set.options.batchSize?(number | undefined) - The number of blocks that will be used to determine the size of batch. Default is 120 blocks.options.confirmations?(number | undefined) - The number of confirmations that events will have to await before they will be passed on.options.startingBlock?(number | undefined) - The starting block number from which the fetching of events will start from. Most probably the block number of the deployed Contract.
* fetch(options?: FetchOptions) => AsyncIterableIterator<Batch<Events>>
Method that return async generator that emits batches of events.
It honors Confirmations. So if Confirmations are enabled and there are confirmed events awaiting to be returned, then the first
batch will return those. Be aware that the in this batch all confirmed events are returned and the batchSize is not really honored here.
Also, it detects and handles blockchain reorganizations if confirmations are enabled.
Parameters:
options(FetchOptions) - Options for fetching the events.options.currentBlock(BlockHeader | undefined) - Is the latest block on a blockchain, serves as optimization if you have already the information available.options.toBlockNumber(number | undefined; default is latest block number) - Number of block to which the events will be fetched to INCLUDING.
Batch interface:
interface Batch<E> {
/**
* Starts with 1 and go up to totalSteps (including).
* If confirmations are enabled, then the first batch is with confirmed events.
*/
stepsComplete: number
/**
* Number of total batches that gonna be emitted
*/
totalSteps: number
stepFromBlock: number
stepToBlock: number
/**
* Actually emitted events.
*/
events: E[]
}
Events
It emits a bunch of events that you might be interested in:
progress(withProgressobject as payload) - as the events are processed in batches, you will get reporting on what batch is being processed and general progress.reorg(only whenconfirmationsare enabled) - informational event that notifies you that there was a blockchain reorganisation that was tackled by your confirmation range.reorgOutOfRange(only whenconfirmationsare enabled) - information event that notifies you that there was a blockchain reorganisation outside of confirmation range and hence your state can be invalid.newConfirmation(only whenconfirmationsare enabled; returnsNewConfirmationEventobject) - information that there is new confirmation for given event.invalidConfirmation(only whenconfirmationsare enabled; returnsInvalidConfirmationsEventobject) - information that during reorganisation that happened in the confirmation range a transaction was dropped.error- general event that is emitted whenever something goes wrong
AutoEventsEmitter<Events> class
Utility class that implements the EventsFetcher interface and takes EventsFetcher instance (ManualEventsEmitter or GroupEventsEmitter classes) and using the NewBlockEmitter automatically triggers
fetch and then emit the fetched events using newEvent.
constructor (fetcher: EventsFetcher<E>, newBlockEmitter: NewBlockEmitter, baseLogger: Logger, options?: AutoEventsEmitterOptions)
Additional options are:
options.serialListeners?(boolean | undefined; default:false) - Defines if the listeners should be processed serially. This effects if you have multiple listeners on the EventsEmitter, where it will be awaited for a listener to finish (eq. if it returns Promise, then to be resolved) before moving to next listeners.options.serialProcessing?(boolean | undefined; default:false) - Defines if the events should be kept in order and processed serially. This will await for the processing of a event to finish before moving to next event.options.autoStart?(boolean | undefined; default:true) - Defines if the EventsEmitter should automatically start listening on events when an events listener fornewEventis attached.
* fetch(currentBlock?: BlockHeader) => AsyncIterableIterator<Batch<Events>>
This is same like for ManualEventsEmitter
Events
It emits all the events that ManualEventsEmitter emits and additionally:
newEvent(withEventLogobject as payload) - the main event which pass to you a ready to be processed event from Contract.
GroupEventsEmitter<Events> class
EventsFetcher implementation that takes other Emitters and group then under one Emitter interface.
The Emitters have to have same batchSize and must not have any newEvent listeners (in AutoEventsEmitter case).
Also, supports ordering of events across the emitters based on the blockchain's blockNumber, transactionIndex and logIndex values.
It re-emits events from the Emitters, but the data of the events are wrapped in object: { name: string, data: any}
Where name is the name of the Emitter the event is coming from and that data is data passed into the emit function.
constructor(eth: Eth, emitters: EventsFetcher<any>[], options?: GroupEmitterOptions)
Parameters:
eth(Eth) - Instance of Web3.jsEthclass defining connection to blockchain.emitters(EventsFetcher<any>[]) - Array of Emitters (eq. eitherManualEventsEmitteror wrappedAutoEventsEmitter) that will be grouped.options?(GroupEmitterOptions | undefined) - Options specifying behavior of the Emitter:options.logger(Logger) - Custom Logger instanceoptions.name(string) - Name of the group used in logs and error messagesoptions.orderedProcessing(boolean) - Defines if the events from emitters ordered using blockNumber, transactionIndex and logIndex to determine order of the events.
* fetch(options?: FetchOptions) => AsyncIterableIterator<Batch<Events>>
Method that return async generator that emits batches of events. Same as for ManualEventsEmitter.fetch().
Events
Share the same events like ManualEventsEmitter, except that all the events are wrapped in object:
{
name: 'name of the emitter that emitted the event',
data: 'the emitted data'
}
Contribute
There are some ways you can make this module better:
- Consult our open issues and take on one of them
- Help our tests reach 100% coverage!





