README
dynamic-alias-resolve-plugin
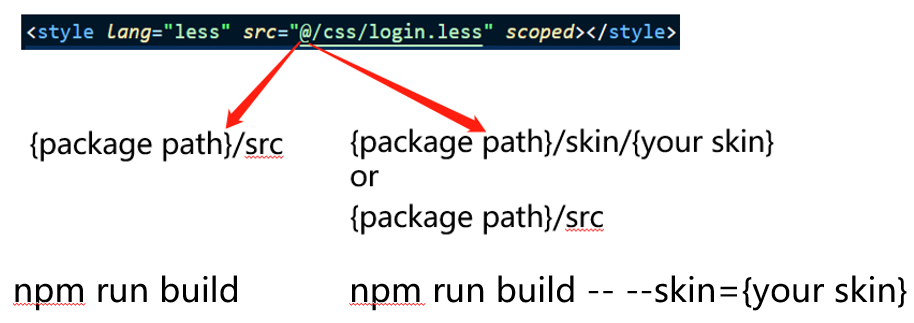
Introduction
Thanks for the help of enhanced-resolve, we can define alias for path, but it's static, in some cases we may want alias point to A path or B path, in other words, we want dynamic alias. enhanced-resolve is based on tapable, so we can write a plugin to make it.
Read this in other languages: english, 简体中文
Prerequisites
This module requires webpack v4 and above.
Installation
npm install -D dynamic-alias-resolve-plugin
Usage
In your webpack config, require() the dynamic-alias-resolve-plugin plugin as follows:
const DynamicAliasResolvePlugin = require("dynamic-alias-resolve-plugin");
and finally, add the plugin to your resolve configuration's plugins array
// https://webpack.js.org/configuration/resolve/#resolveplugins
resolve: {
plugins: [
new DynamicAliasResolvePlugin({
// alias you want to make it dynamic
alias: "@",
// pathA or pathB should be replaced with real path
// "request" is raw request object from enhanced-resolve
// "alias" is matched alias of current request.(eg. "@" in "@/login.less")
dynamic: (request, alias) => "pathA or PathB",
// we just want less file to be handled by this plugin
pattern: /\.less$/,
}),
];
}
Options
| properties | type | default |
|---|---|---|
| alias | Array<string> | ['@'] |
| dynamic | function(request,alias)=>string|null|false|undefined | ()=>null |
| pattern | RegExp | /.*/ |
| extensions | Array<string> | ["js", "mjs", "ts", "jsx", "tsx"] |
Description Of Options
alias
alias you want to make it dynamic
dynamic
return value should be absolute path,all false value('',false,null) will be ignored. request is raw enhanced-resolve request object, alias is current alias you want make it dynamic. (eg. "@" in "@/login.less")
pattern
files needs handled by this plugin
extensions
When we import a module we always ignore the extension, for instance, if we want to import something from {path}/a.js we just write import {something} from {path}/a instead of import {something} from {path}/a.js, which is convenient. However, when we resolve a module to an absolute path, we must have the file extension info. If you specified this option, we will try to match extensions that you specied when we encounter a module that don't have a file extension, or we will use the default extensions(["js", "mjs", "ts", "jsx", "tsx"]).