README
joypad.js 



JavaScript library that lets you connect and use various gaming controllers with browsers that support the Gamepad API.
Less than 5KB in size with zero dependencies and support for button press, axis movement events and vibration play effect.
Examples
Working examples can be found in the examples folder in the repo -
connection.html - Gamepad connection example.
jumpingBall.html - Button press example (with custom button mapping).
movingBall.html - Axis (analog stick) movement example.
vibration.html - Vibration play effect example.
Installation
via npm
npm install joypad.js --save
via yarn
yarn add joypad.js
Or, download the latest version and include joypad.min.js to your project.
Usage
Once joypad.js is installed and included in your project it becomes available on the global scope - window.joypad.
If you're working with ES6 or Common JS modules you can include the library as follows -
import 'joypad.js'; // ES6
require('joypad.js'); // Common JS
Once set up you can start listening to joypad.js events like so -
joypad.on('connect', e => {
const { id } = e.gamepad;
console.log(`${id} connected!`);
});
API
joypad.instances {object}
Lists all the connected Gamepad instances. Each instance defines an individual gamepad or controller with access to information such as button presses, axis movements, id, index etc.
console.log(joypad.instances); // {0: Gamepad {id: "Wireless Contr..", index: 0 ..}, 1: Gamepad {id: "Wireless Contr..", index: 1 ..}}
joypad.on(event, callback) {method}
Used to attach event listeners to joypad.js events. It takes 2 parameters, an event name (which is a string) and a callback function which is fired whenever the specified event is triggered.
joypad.on('button_press', e => {
const { buttonName } = e.detail;
console.log(`${buttonName} was pressed!`);
});
This returns a reference to the unsubscribe method which can be used to unsubscribe from the specified event.
const buttonPressEvent = joypad.on('button_press', e => { ... });
const gameOver = () => {
buttonPressEvent.unsubscribe();
};
View all of the supported events here.
joypad.set({settings}) {method}
Used to set the global settings for joypad.js such as the threshold for axis movement and options for vibration play effect. It expects a single parameter, which is an object with the required setting values to be applied.
joypad.set({
axisMovementThreshold: 0.3
});
Note: To make sure that your applied settings have the desired effect, please use this method before initialising your event listeners.
View all of the available settings here.
joypad.settings {object}
Lists all the global settings applied to joypad.js.
console.log(joypad.settings); // {axisMovementThreshold: 0.3, vibration: {..}}
joypad.vibrate(gamepad, options) {method}
Triggers the vibration play effect for a particular gamepad (which is an instance of Gamepad). The options parameter is an object with the required vibration setting values to be applied.
joypad.on('connect', e => {
const { gamepad } = e;
const options = {
startDelay: 500,
duration: 2000,
weakMagnitude: 1,
strongMagnitude: 1
};
joypad.vibrate(gamepad, options);
});
Note: Options passed to the vibrate method will override the global vibration settings.
To know about all the options supported by the vibrate method click here.
Note: Since the Gamepad API is in very early stages, the vibrate method might not work on most browsers.
joypad.trigger(event, data) {method}
Emulates an event with the provided data.
joypad.trigger('button_press', {
detail: {
buttonName: 'button_0'
}
});
Events
connect
Fired whenever a controller is connected.
disconnect
Fired whenever a controller is disconnected.
button_press
Fired whenever a controller's button is pressed.
joypad.js supports the standard gamepad button layout which is supported by most controllers in which button locations are laid out in a left cluster of four buttons, a right cluster of four buttons , a center cluster of three buttons (some controllers have four) and a pair of front facing buttons (shoulder buttons) on the left and right side of the gamepad.
Note: Since the Gamepad API is in very early stages, the standard gamepad button layout may differ from browser to browser.
The following image and table describes the default button mappings as on Chrome -
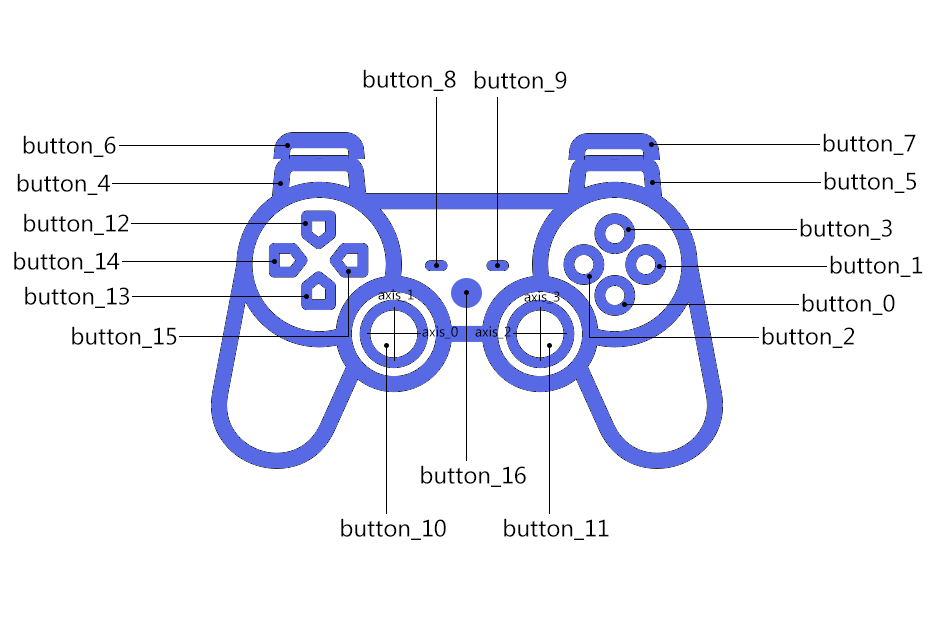
| Button | Location |
|---|---|
| button_0 | Bottom button in right cluster |
| button_1 | Right button in right cluster |
| button_2 | Left button in right cluster |
| button_3 | Top button in right cluster |
| button_4 | Shoulder left front button |
| button_5 | Shoulder right front button |
| button_6 | Shoulder left back button |
| button_7 | Shoulder right back button |
| button_8 | Left button in center cluster |
| button_9 | Right button in center cluster |
| button_10 | Left stick pressed button |
| button_11 | Right stick pressed button |
| button_12 | Top button in left cluster |
| button_13 | Bottom button in left cluster |
| button_14 | Left button in left cluster |
| button_15 | Right button in left cluster |
| button_16 | Vendor button 1 |
| button_17 | Vendor button 2 |
If you would like to set custom button mappings for better cross browser support, you can use the customButtonMapping setting.
axis_move
Fired whenever a controller's axis (analog stick) is moved.
The standard button layout has four axes associated with a pair of analog sticks, one on the left and one on the right.
| Axis | Location |
|---|---|
| 0 | Horizontal axis for left stick (negative left/positive right) |
| 1 | Vertical axis for left stick (negative up/positive down) |
| 2 | Horizontal axis for right stick (negative left/positive right) |
| 3 | Vertical axis for right stick (negative up/positive down) |
Settings
vibration {object}
The vibration option sets the parameters for the vibration play effect globally. Currently there is support for a dual-rumble effect. A dual-rumble effect is a fixed-length, constant-intensity vibration effect intended for an actuator of type dual-rumble. Dual-rumble effects are defined by four parameters -
startDelay {number}
Sets the duration of the delay in milliseconds after which the vibration effect is started.
duration {number}
Sets the duration of the vibration effect in milliseconds.
weakMagnitude {number}
Sets the rumble intensity of the high-frequency (weak) rumble motors, normalized to the range [0.0, 1.0].
strongMagnitude {number}
Sets the rumble intensity of the low-frequency (strong) rumble motors, normalized to the range [0.0, 1.0].
joypad.set({
vibration: {
startDelay: 500,
duration: 3000,
weakMagnitude: 1,
strongMagnitude: 1
}
});
Note: To override the global vibration settings you can pass these parameters to the
joypad.vibratemethod.
Note: Since the Gamepad API is in very early stages, the vibrate method might not work on most browsers.
axisMovementThreshold {number}
Sets the threshold for axis (analog stick) movement normalized to the range [0.0, 1.0]. Higher the value, more rigid will be the movement.
To test the calibration of the analong sticks you can check out html5gamepad.com and decide a suitable value for the axis movement threshold.
joypad.set({
axisMovementThreshold: 0.3
});
customButtonMapping {object}
Used to set custom button mapping for better cross browser button mappings support.
function setCustomButtonMapping() {
if (browserIs('Firefox')) {
return {
button_0: 1,
button_7: 11,
button_8: 12
}
} else {
return null;
}
};
joypad.set({
customButtonMapping: setCustomButtonMapping()
});
Browsers support
 Edge Edge |
 Firefox Firefox |
 Chrome Chrome |
 Safari Safari |
 Opera Opera |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12+ | 29+ | 25+ | 10.1+ | 24+ |
Testing
joypad.js uses the jest test runner. Run the following command to initiate it -
npm test
Contributors
Arun Michael Dsouza |
Antoine Bluchet |
Bart Nagel |
|---|
Support
If you'd like to help support the development of the project, please consider backing me on Patreon -
License
MIT Licensed
Copyright (c) 2019 Arun Michael Dsouza (amdsouza92@gmail.com)
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
All icons and images have been taken from freepik.com.
