README
spok 
Checks a given object against a given set of specifications to keep you from writing boilerplate tests.
var test = require('tape')
var spok = require('spok')
// this would be returned from a function you are testing
var object = {
one : 1
, two : 2
, three : 3
, four : 4
, helloWorld : 'hello world'
, anyNum : 999
, anotherNum : 888
, anArray : [ 1, 2 ]
, anotherArray : [ 1, 2, 3 ]
, anObject : {}
}
// custom specification
function hasThreeElements(a) {
return a.length === 3
}
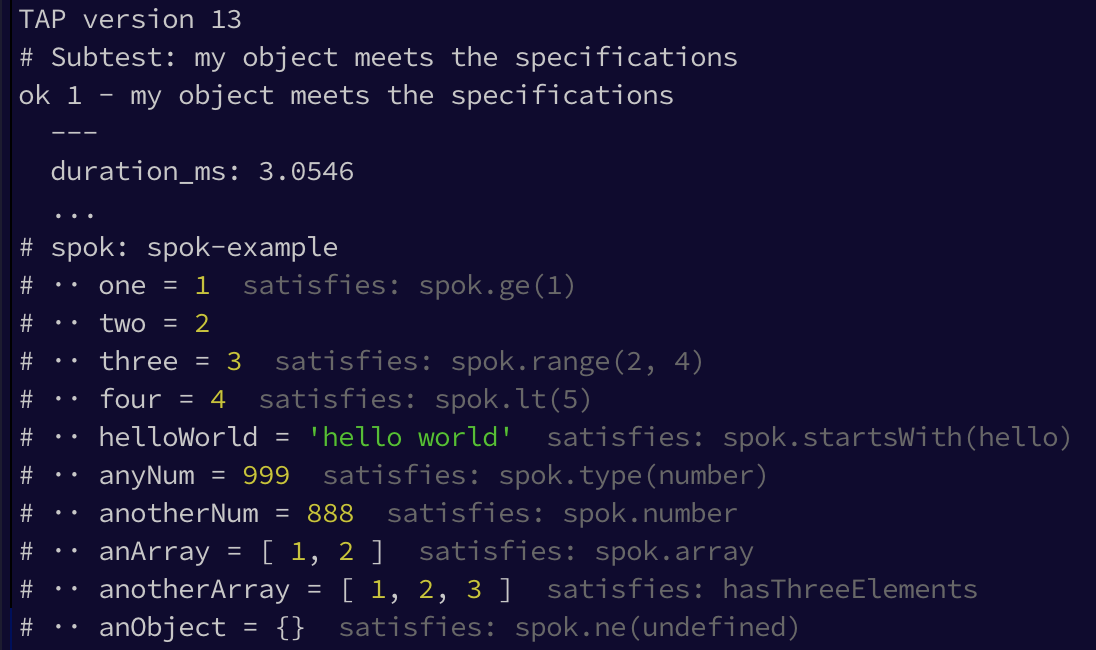
test('my object meets the specifications', function(t) {
spok(t, object, {
$topic : 'spok-example'
, one : spok.ge(1)
, two : 2
, three : spok.range(2, 4)
, four : spok.lt(5)
, helloWorld : spok.startsWith('hello')
, anyNum : spok.type('number')
, anotherNum : spok.number
, anArray : spok.array
, anotherArray : hasThreeElements
, anObject : spok.ne(undefined)
})
t.end()
})
Installation
npm install spok
Cypress/Chai Expect Support
Spok can be used out of the box with expect, for instance when running tests with
cypress.io.
Simply create a custom assert function and pass it to spok. The main difference to running
tests with tape is that if a single property in the compared object doesn't match the test
fails immediately.
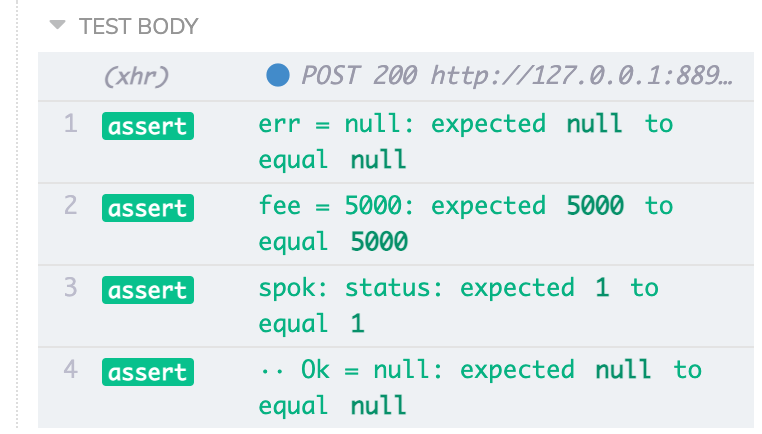
import spok from 'spok'
const t = spok.adapters.chaiExpect(expect)
spok(t, meta, {
err: null,
fee: 5000,
status: {
Ok: null,
},
})
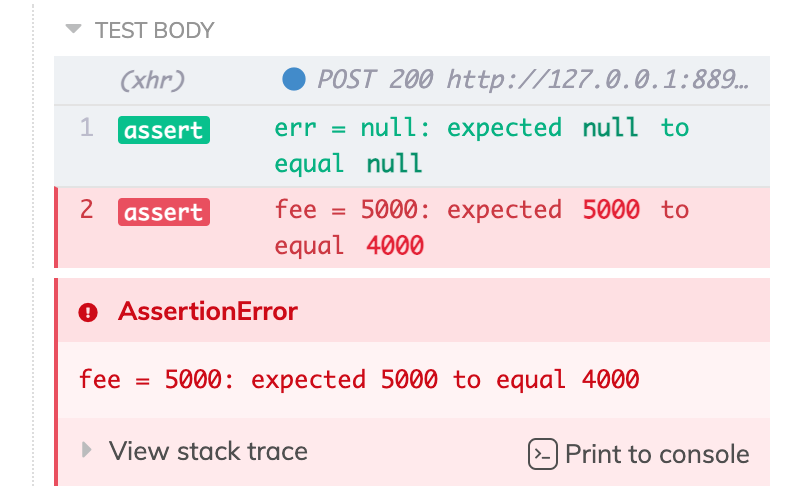
spok(t, meta, {
err: null,
fee: 4000,
status: {
Ok: null,
},
})
Why not just deepEqual?
deepEqual works great for most cases, but in some cases you need more control, i.e.
- values don't exactly match, but are in a given range
- you want to provide a predicate to determine if a value is correct or not
- you only want to check a subset of values contained in the object
Adjusting Print Details
By default spok prints the specification that a particular assertion satisified, i.e. satisfies: spok.range(2, 4).
You can turn that off via spok.printSpec = false.
On the other hand if you want more details about the satisified spec do spok.printDescription = true instead to get
spok to print things like satisfies: spok.range(2, 4) 2 <= value <= 4.
Specs and descriptions are printed in gray so you can focus on the actual values of the test output.
Table of Contents generated with DocToc
spok provides a few common specification functions. However you can write your own functions as well, just return true
if specification was satisfied and false if not (see example above).
If you write a specification function that would be useful to others please add it along with a test and provide a PR.
spok.* comparison function names are derived from bash comparison
operators to make them easier to remember.
API
spok
Checks the given specifications against the object.
When the tests are run the actual values are printed to verify visually while each provided specification is validated and a test failure caused if one of them fails.
Parameters
tObject which has assertion functionsequalanddeepEqual(to compare objects) - use tap, tape, assert or any other library that has those and thus is compatibleobjObject the object to verify the specifications againstspecificationsObject the specifications to verify
spok.any
Version of spok that is less strict about the relation of the
specification type, namely it allows overriding the type manually or
derives it from the supplied parameter.
Use ONLY when you cannot adjust the types, so plain spok works.
spok.range
Specififies that the given number is within the given range, i.e. min<= x <=max.
var spec = {
x: spok.range(1, 2) // specifies that x should be >=1 and <=2
}
Parameters
spok.gt
Specififies that a number is greater than the given criteria.
var spec = {
x: spok.gt(1) // specifies that x should be >1
}
Parameters
nNumber criteria
spok.ge
Specififies that a number is greater or equal the given criteria.
var spec = {
x: spok.ge(1) // specifies that x should be >=1
}
Parameters
nNumber criteria
spok.lt
Specififies that a number is less than the given criteria.
var spec = {
x: spok.lt(1) // specifies that x should be < 1
}
Parameters
nNumber criteria
spok.le
Specififies that a number is less or equal the given criteria.
var spec = {
x: spok.le(1) // specifies that x should be <=1
}
Parameters
nNumber criteria
spok.ne
Specifies that the value is not equal another.
var spec = {
x: spok.ne(undefined) // specifies that x should be defined
}
Parameters
valueAny criteria
spok.gtz
Specifies that the value is greater than zero
var spec = {
x: spok.gtz
}
spok.gez
Specifies that the value is greater or equal zero
var spec = {
x: spok.gez
}
spok.ltz
Specifies that the value is less than zero
var spec = {
x: spok.ltz
}
spok.lez
Specifies that the value is less or equal zero
var spec = {
x: spok.lez
}
spok.type
Specifies that the input is of a given type.
var spec = {
x: spok.type('number') // specifies that x should be a Number
}
Parameters
tString expected type
spok.array
Specifies that the input is an array.
var spec = {
x: spok.array // specifies that x should be an Array
}
spok.arrayElements
Specifies that the input is an array with a specific number of elements
var spec = { x: spok.arrayElements(2) // specifies that x should be an Array with 2 elements }
Parameters
nNumber number of elements
spok.arrayElementsRange
Specifies that the input is an array with a number of elements in a given range
var spec = { x: spok.arrayElementsRange(2, 4) // specifies that x should be an Array with 2-4 elements }
Parameters
spok.number
Specifies that the input of type number and isNaN(x) returns false.
var spec = {
x: spok.number // specifies that x should be a Number
}
spok.string
Specifies that the input is a string.
var spec = {
x: spok.string // specifies that x should be a String
}
spok.function
Specifies that the input is a function.
var spec = {
x: spok.function // specifies that x should be a function
}
spok.definedObject
Specifies that the input is an object and it is not null.
var spec = {
x: spok.definedObject // specifies that x is a non-null object
}
spok.startsWith
Specifies that the string starts with the specified substring.
NOTE: only available with node.js which has an ES6 startsWith function
var spec = {
x: spok.startsWith('hello') // specifies that x should start with 'hello'
}
Parameters
whatString substring the given string should start with
spok.endsWith
Specifies that the string ends with the specified substring.
NOTE: only available with node.js which has an ES6 endsWith function
var spec = {
x: spok.endsWith('hello') // specifies that x should start with 'hello'
}
Parameters
whatString substring the given string should start with
spok.test
Specifies that the string needs to match the given regular expression.
var spec = {
x: spok.test(/hello$/) // specifies that x should match /hello$/
}
Parameters
regexRegExp regular expression against which the string is checked viatest
spok.defined
Specifies that a value is defined, i.e. it is neither null nor undefined.
var spec = {
x: spok.defined
}
spok.notDefined
Specifies that a value is notDefined, i.e. it is either null or notDefined.
var spec = {
x: spok.notDefined
}
License
MIT