README
SvelteFire
Cybernetically enhanced Firebase apps 💪🔥
Basics
- Use Firebase declaratively in Svelte components.
- Handle complex relational data between Auth and Firestore.
- Built in loading & fallback states for async data. (Similar to React Suspense)
- Automatic data disposal to prevent memory/cost leaks, plus enhanced logging.
- Automatic performance monitoring & Google Analytics.
Psuedo Example
Handle multiple levels of async relational data (and their loading & fallback states) entirely from the Svelte HTML.
<!-- 1. 🔥 Firebase App -->
<FirebaseApp {firebase}>
<!-- 2. 😀 Get the current user -->
<User let:user>
<p>Howdy, {user.uid}</p>
<!-- 3. 📜 Get a Firestore document owned by a user -->
<Doc path={`posts/${user.uid}`} let:data={post} let:ref={postRef}>
<h2>{post.title}</h2>
<!-- 4. 💬 Get all the comments in its subcollection -->
<Collection path={postRef.collection('comments')} let:data={comments}>
{#each comments as comment}
{/each}
...
Quick Start
Grab the sveltefire-template.
npx degit codediodeio/sveltefire-template fireapp
cd fireapp
npm install
or install from NPM:
npm install sveltefire
And do not forget to install firebase dependencies
npm install firebase
Please read the Installation guide for any frequenty encountered issues when integrating in a svelte project.
Create a project at https://firebase.google.com/ and grab your web config:
Opt-in to the following services from the Firebase console to run the demo.
- Anonymous Login under authentication -> sign-in method
- Cloud Firestore under database. Make sure it's in test mode (or provide write access to the
posts/collection using Security Rules).
Open App.svelte and replace the firebaseConfig prop with your Firebase project credentials. Run it:
npm run dev
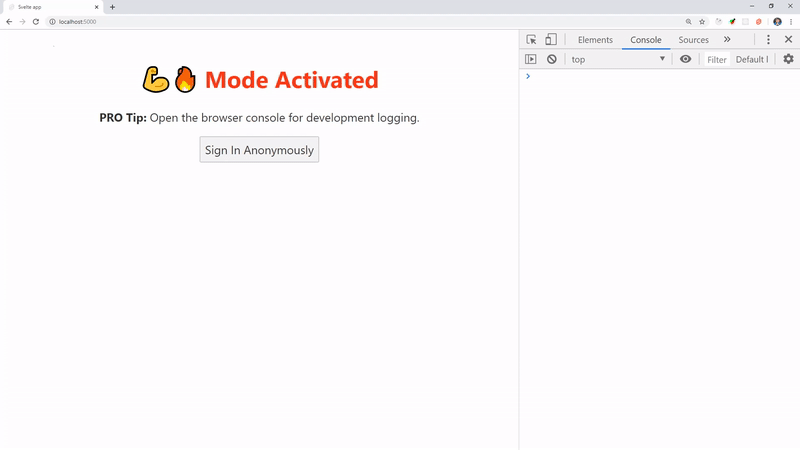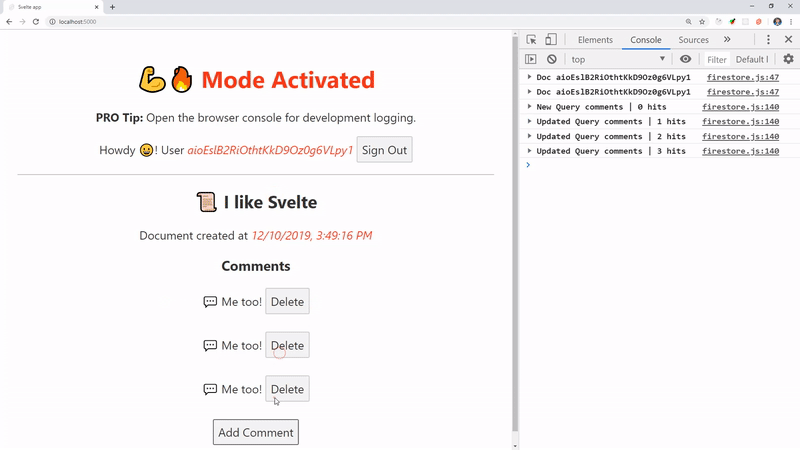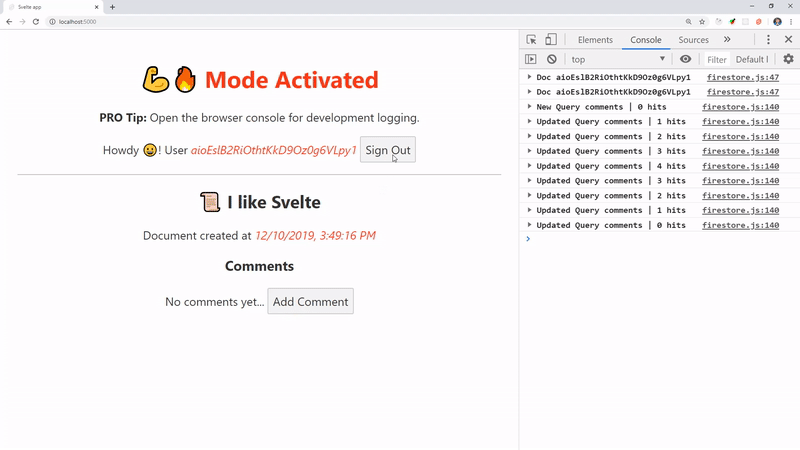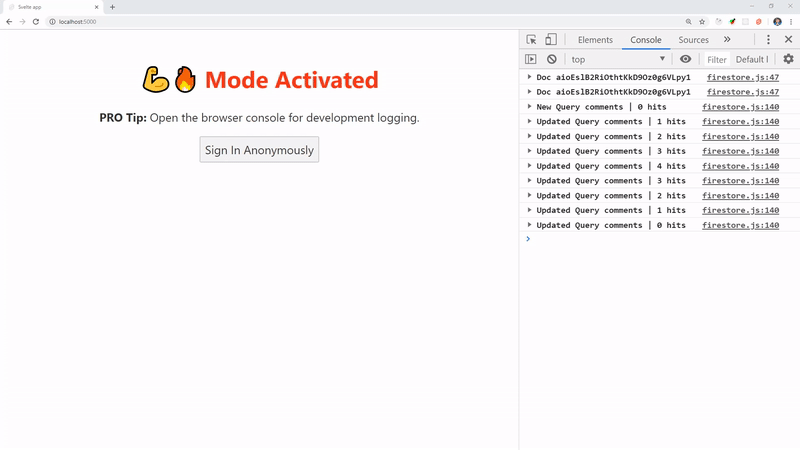
Congrats! You are now running an authenticated realtime Svelte app.
👀 See the Install Guide for additional options.
Concepts and Examples
SvelteFire allows you to use Firebase data anywhere in the Svelte component without the need to manage async state, promises, or streams.
Slots
Slots render different UI templates based on the state of your data. The loading state is shown until the first response is received from Firebase. The fallback state is shown if there is an error or timeout.
In most cases, state flows from loading -> default. For errors, non-existent data, or high-latency, state flows from loading -> fallback maxWait default is 10000ms).
<Doc path={'foods/ice-cream'}>
<!-- Default Slot -->
Data loaded, yay 🍦!
<!-- Only shown when loading -->
<div slot="loading"></div>
<!-- Shown on error or if nothing loads after maxWait time-->
<div slot="fallback"></div>
</Doc>
Error handling made easy:
<Doc {path} let:error>
<div slot="fallback">
😔 This doc cannot be read {error}
</div>
</Doc>
Loading state made easy:
<Doc {path}>
<div slot="loading">
⌛
</div>
</Doc>
You can bypass the loading state entirely by passing a startWith prop.
<Doc {path} startWith={ {flavor: 'vanilla'} }>
Slot Props
Slot props pass data down to children in the component tree. SvelteFire exposes the data you needed for the UI and the reference to performance writes. For example, let:data is the document data, while ={icecream} is the variable name you use to reference it in your code. Use ref to set, update, or delete the document at this path.
<Doc path={`food/ice-cream`} let:data={icecream} let:ref={docRef}>
{icecream.flavor} yay 🍦!
<button on:click={() => docRef.delete()}>Delete</button>
</Doc>
Events
Events emit data up to the parent. You can use components as a mechanism to read documents without actually rendering UI. Also useful for trigging side effects.
<Doc path={'food/ice-cream'} on:data={(e) => console.log(e.detail.data)} />
Reactive
Components are reactive. When props change, they unsubscribe from the last stream and start a new one. This means you can change the document path or query function by simplying changing a prop value.
Example: Collections have special slot props for pagination called first and last. Use them to create reactive pagination queries.
<script>
let query = (ref) => ref.orderBy('flavor').limit(3)
function nextPage(last) {
query = (ref) => ref.orderBy('flavor').startAfter(last.flavor).limit(3);
}
</script>
<Collection path={'foods'} {query} let:data let:last>
{#each data as food}
{food.name}
{/each}
<button on:click={() => nextPage(last) }>Next</button>
</Collection>
Stores
Stores are used under the hood to manage async data in components. It's an advanced use-case, but they can be used directly in a component script or plain JS.
<script>
import { collectionStore } from 'sveltefire';
const data = collectionStore('things', (ref => ref.orderBy('time') ));
data.subscribe(v => doStuff(v) )
</script>
Firebase App Context
The Firebase SDK is available via the Context API under the key of firebase using the getFirebase function.
const app = getContext('firebase').getFirebase();
const db = app.firestore();
const auth = app.auth();
API
<FirebaseApp>
Sets Firebase app context
Props:
- firebase Firebase instance. If empty, it will attempt to use
window.firebase. - perf Starts Firebase Performance Monitoring
- analytics Starts Firebase/Google Analytics
<FirebaseApp firebase={firebase} perf analytics>
<!-- default slot -->
</FirebaseApp>
<User>
Listens to the current user.
Props:
- persist user in
sessionStorageorlocalStorage. Can prevent flash if user refreshes browser. Defaultnull;
Slots:
- default slot shown to signed-in user
- signed-out shown to signed-out user
Slot Props & Events:
- user current FirebaseUser or
null - auth Firebase Auth to call login methods.
<User persist={sessionStorage} let:user={user} let:auth={auth} on:user>
{user.uid}
<div slot="signed-out"></div>
</User>
<Doc>
Retrieves and listens to a Firestore document.
Props:
- path (required) - Path to document as
stringOR a DocumentReference i.edb.doc('path') - startWith any value. Bypasses loading state.
- maxWait
numbermilliseconds to wait before showing fallback slot if nothing is returned. Default 10000. - once single read execution, no realtime updates. Default
false. - log debugging info to the console. Default
false. - traceId
stringname that runs a Firebase Performance trace for latency.
Slots:
- default slot shown when document is available.
- loading when waiting for first response.
- fallback when error occurs.
Slot Props & Events:
- data Document data
- ref DocumentReference for writes
- error current error
<Doc
path={'posts/postId'}
startWith={defaultData}
log
traceId={'postRead'}
let:data={myData}
let:ref={myRef}
on:data
on:ref
>
{post.title}
<span slot="loading">Loading...</span>
<span slot="fallback">Error...</span>
</Doc>
<Collection>
Retrieves and listens to a Firestore collection or query.
Props:
- path (required) to document as
stringORCollectionReferencei.edb.collection('path') - query
function, i.e (ref) => ref.where('age, '==', 23) - startWith any value. Bypasses loading state.
- maxWait
numbermilliseconds to wait before showing fallback slot if nothing is returned. Default 10000. - once single read execution, no realtime updates. Default
false. - log debugging info to the console. Default
false. - traceId
stringname that runs a Firebase Performance trace for latency.
Slots:
- default slot shown when document is available.
- loading when waiting for first response.
- fallback when error occurs.
Slot Props & Events:
- data collection data as array.
- ref CollectionReference for writes
- first the first result in the query, useful for pagination.
- last the last result in the query, useful for pagination.
- error current error
<Collection
path={'comments'}
query={ (ref) => ref.orderBy(date).limit(10) }
traceId={'readComments'}
log
let:data={comments}
let:ref={commentsRef}
let:last={firstComment}
let:first={lastComment}
on:data
on:ref
>
{#each comments as comment}
{comment.text}
{/each}
<div slot="loading">Loading...</div>
<div slot="fallback">
Unable to display comments...
</div>
</Collection>
Note: Each data item in the collection contains the document data AND fields for the id and ref (DocumentReference).
<StorageRef>
Retrives a downloadURL and metadata from Firebase storage.
Props:
- path (required) to file in storage i.e
images/mountain.jpgor a Reference - meta include metadata with file. Default
false. - startWith start with a default URL. Pass an object like
{ url: someURL }
Slots:
- default slot shown when downloadURL is available.
- loading shown when waiting for response.
- fallback shown when error occurs.
Slot Props & Events:
- downloadURL url to resource
- metadata file metadata
- ref Storage Reference for direct access
<StorageRef {path} let:downloadURL let:ref meta let:metadata>
<img src={downloadURL} />
<div slot="loading">
Loading...
</div>
<div slot="fallback">
Error
</div>
</StorageRef>
<UploadTask>
Creates an UploadTask that transmits a file to Firebase storage.
Props:
- path (required) to upload to i.e "images/mountain.jpg" or a Reference
- file file to upload as a
FileobjectBloborUnit8Array.
Slots:
- default slot shown while task is created.
- complete shown when task state is
successand url is available. - fallback shown when error occurs or upload is cancelled.
Slot Props & Events:
- snapshot snapshot of upload, useful for monitoring progress.
- task Firebase upload task. Use it to pause, resume, and cancel.
task.pause() - downLoadURL url to uploaded file.
<UploadTask {file} {path} let:task let:snapshot let:downloadURL={url}>
Uploading your file...
Progress: {(snapshot.bytesTransferred / snapshot.totalBytes) * 100} %
<div slot="complete">
Success! Download here {url}
</div>
<div slot="fallback">
Error or canceled
</div>
</UploadTask>