README
TeX Math Parser
TeX Math Parser parses TeX math into a MathJS expression tree which can then be further manipulated and evaluated by MathJS. The library also provides convenience functions for directly evaluating TeX math with MathJS.
This library works well as a bridge between MathQuill and MathJS. Use this library to parse the TeX formatted output from MathQuill into a format that can be manipulated by MathJS.
TeX Features
- Common operators available in TeX math mode:
+,-,*,^,/,\cdot - Basic functions:
\sqrt,\frac,\sin,\cos,\tan,\csc,\sec,\cot,\arcsin,\arccos,\arctan,\log,\ln,\det - Custom functions implemented with MathJS:
eigenvectors,eigenvalues,cross,proj,comp,norm,inv- Since these are custom functions, they should be formatted as
\operatorname{function}in TeX.
- Since these are custom functions, they should be formatted as
- Constants:
\pi,e - Environnements:
matrix - Variables
^Tis interpreted as the transpose operation
Browser Support
Any browser with ES6 support.
Installation
Install with NPM:
npm install tex-math-parser
or link to it from a CDN:
<script src=https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/tex-math-parser></script>
Usage
Given the following TeX source string:
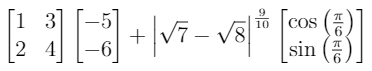
\begin{bmatrix}1&3\\2&4\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}-5\\-6\end{bmatrix}+\left|\sqrt{7}-\sqrt{8}\right|^{\frac{9}{10}}\begin{bmatrix}\cos\left(\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\\\sin\left(\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\end{bmatrix}
Load the package and escape the string:
import { parseTex, evaluateTex, evaluateTexFormatted } from 'tex-math-parser' // ES6 module
// Make sure to escape the string!
const escapedTex = String.raw`\begin{bmatrix}1&3\\2&4\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}-5\\-6\end{bmatrix}+\left|\sqrt{7}-\sqrt{8}\right|^{\frac{9}{10}}\begin{bmatrix}\cos\left(\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\\\sin\left(\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\end{bmatrix}`; // ES6 raw template string
Evaluate the string and get an answer in TeX:
const texAnswer = evaluateTex(escapedTex);
console.log(texAnswer);
// \begin{bmatrix}-22.812481734548864\\-33.89173627896382\\\end{bmatrix}
Parse the string and get a a MathJS expression tree:
const mathJSTree = parseTex(escapedTex);
Variables
If the TeX string contains variables, the value of the variables must be supplied when evaluating.
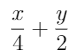
const texStr = String.raw`\frac{x}{4}+\frac{y}{2}`;
const answer = evaluateTex(texStr, {x: 2, y: 1});
console.log(answer); // 1
API
evaluateTex(texStr: string, scope: Object)
Evaluate a TeX string, replacing any variable occurences with their values in scope. The answer is returned as a TeX string.
parseTex(texStr: string)
Convert a TeX string into a MathJS expression tree. The function returns the root node of the tree.
Details
parseTex first lexes the TeX string into tokens, which are then passed to the parser to create the expression tree. A context-free grammar for the simplified version of TeX math used by the parser is as follows:
expr = term ((PLUS | MINUS) term)*
term = factor ((CDOT factor | primary )* // primary and factor must both not be NUMBERs
factor = MINUS? power
power = primary (CARET primary)*
primary = grouping
| environnment
| frac
| function
| NUMBER
| VARIABLE
grouping = LEFT LPAREN expr RIGHT RPAREN
| LPAREN expr RPAREN
| LBRACE expr RBRACE
| LEFT BAR expr RIGHT BAR
| BAR expr BAR
environnment = matrix
frac = FRAC LBRACE expr RBRACE LBRACE expr RBRACE
function = (SQRT | SIN | COS | TAN ...) grouping
matrix = BEGIN LBRACE MATRIX RBRACE ((expr)(AMP | DBLBACKSLASH))* END LBRACE MATRIX RBRACE
As the grammar is not left-recursive, the parser was implemented as a recursive descent parser with each production being represented by a separate function. This keeps the parser easily extensible.