README
aio-cli-plugin-aep
A plugin for CRUD operations on aep resources
Follow the steps below to start using this plugin.
1. Set up necessary dependencies for npm to work
Install brew:
$ /bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install.sh)"Install npm:
$ brew install npmInstall yarn:
$ npm install --global yarnUpgrade yarn:
$ npm upgrade --global yarn
2. Set up necessary adobe I/O dependencies
Install aio-cli core libraries
$ npm install -g @adobe/aio-cliInstall aep aio plugin
$ npm install -g @adobe/aio-cli-plugin-aepLink aep with aio
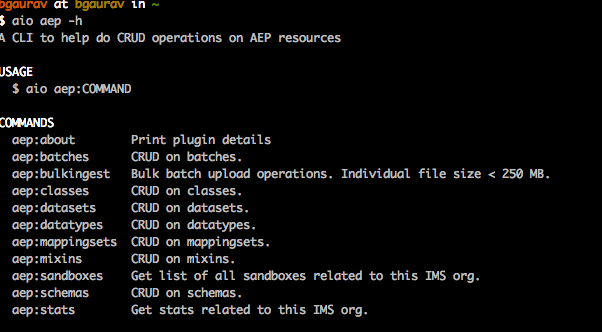
$ aio plugins:install @adobe/aio-cli-plugin-aepWhen you run
$ aio aep -hnow you should be able to see aep as an available plugin with its available sub-commands.
3. Set up adobe I/O (PROD/STG/INT) integration
For PROD
Go to https://console.adobe.io/integrations and create a production integration for test
Follow the instructions on https://www.adobe.io/apis/experienceplatform/home/tutorials/alltutorials.html#!api-specification/markdown/narrative/tutorials/authenticate_to_acp_tutorial/authenticate_to_acp_tutorial.md
to get the necessary I/O config credentials
Create a
config.jsonfile with the following content and replacing the placeholders with actual values. Thejwt_payloadelement in the following json, you can directly copy from your Adobe I/O integrations page mentioned in step 1.
{
"client_id": "${your_client_id}",
"client_secret": "${your_client_secret}",
"jwt_payload": {
"exp": ${your_expiration_time},
"iss": "${your_org@AdobeOrg}",
"sub": "${your_tech_id@techacct.adobe.com}",
"https://ims-na1.adobelogin.com/s/ent_dataservices_sdk": true,
"aud": "https://ims-na1.adobelogin.com/c/${your_client_id}"
},
"token_exchange_url": "https://ims-na1.adobelogin.com/ims/exchange/jwt/",
"jwt_private_key": "${path to your private.key file used in Adobe I/O integration}",
"x-sandbox-id": "${your_sandbox_id}",
"x-sandbox-name": "${your_sandbox_name}",
"env": "prod"
}
Run the following commands now (in the particular order)
$ aio config:set jwt-auth ${path_to_the_above_config.json} --file --json$ aio jwt-auth:access-token
For STG/INT (This sample is for INT)
Go to https://console-stage.adobe.io/integrations and create a production integration for test
Follow the instructions on https://www.adobe.io/apis/experienceplatform/home/tutorials/alltutorials.html#!api-specification/markdown/narrative/tutorials/authenticate_to_acp_tutorial/authenticate_to_acp_tutorial.md
to get the necessary I/O config credentials
Create a
config.jsonfile with the following content and replacing the placeholders with actual values. Thejwt_payloadelement in the following json, you can directly copy from your Adobe I/O integrations page mentioned in step 1.
{
"client_id": "${your_client_id}",
"client_secret": "${your_client_secret}",
"jwt_payload": {
"exp": ${your_expiration_time},
"iss": "${your_org@AdobeOrg}",
"sub": "${your_tech_id@techacct.adobe.com}",
"https://ims-na1-stg1.adobelogin.com/s/ent_dataservices_sdk": true,
"aud": "https://ims-na1-stg1.adobelogin.com/c/${your_client_id}"
},
"token_exchange_url": "https://ims-na1-stg1.adobelogin.com/ims/exchange/jwt/",
"jwt_private_key": "${path to your private.key file used in Adobe I/O integration}",
"x-sandbox-id": "${your_sandbox_id}",
"x-sandbox-name": "${your_sandbox_name}",
"env": "int"
}
Run the following commands now (in the particular order)
$ aio config:set jwt-auth ${path_to_the_above_config.json} --file --json$ aio jwt-auth:access-token
4. Finally run this simple command to list datasets in your org to make sure the configuration is all correct
$ aio aep:datasets:list
Output would look something like...
{
'abc': {
tags: {
targetDataSetId: ['abc'],
'aep/siphon/partitions': [],
'adobe/pqs/table': ['abc'],
sandboxId: ['abc'],
mappingId: ['abc'],
acp_validationContext: ['enabled']
},
imsOrg: 'abc@AdobeOrg',
name: 'Mapping DataSet_abc',
namespace: 'ACP',
state: 'DRAFT',
lastBatchId: 'abc',
lastBatchStatus: 'success',
version: '1.0.3',
created: 1573866068596,
updated: 1573866132606,
createdClient: 'acp_foundation_connectors',
createdUser: 'abc@AdobeID',
updatedUser: 'acp_foundation_dataTracker@AdobeID',
lastSuccessfulBatch: 'abc',
viewId: 'abc',
aspect: 'production',
status: 'enabled',
fileDescription: {
persisted: false
},
files: '@/dataSets/abc/views/abc/files',
schemaMetadata: {
primaryKey: [],
delta: [],
dule: [],
gdpr: []
},
schemaRef: {
id: 'https://ns.adobe.com/acponboarding/schemas/abc',
contentType: 'application/vnd.adobe.xed-full+json;version=1'
},
streamingIngestionEnabled: 'false'
},
...
You can choose not to read the following additional information.
Additional read
The last command would generate a new access_token value and place it in appropriate folder for every command to read.
Think of it as the same parameter we pass in the Authorization header on postman/Curl.
You can also get the access_token manually and use the following command to set it. No need to do this if you have done step 2.
Please follow the instructions as suggested in this article, to get the access_token https://www.adobe.io/apis/experienceplatform/home/tutorials/alltutorials.html#!api-specification/markdown/narrative/tutorials/authenticate_to_acp_tutorial/authenticate_to_acp_tutorial.md#generate-access-token
$ aio config:set jwt-auth.access_token ${your_access_token_generated_through_adobeI/O_integration}
Additionally if you want to have multiple integrations and want the ability to quickly switch between them, create multiple config.json files and place each one of them in a corresponding folder
in your root directory with aprropriate name.
For example, if you want to create an integration with name 'abc'. Please place the corresponding config.json file in /Users/${your_user_name}/abc. And then run the command
$ aio aep:switch-config:set -n=abc
5. Run inside a docker container: To run this plugin as a docker image
DockerFile location:
https://github.com/adobe/aio-cli-plugin-aep/blob/master/DockerfileBuild image: From the folder where dockerFile is located
$ docker build -t aio-cli-plugin-aep .Create a config.json file (based on whether you want STG/INT or PROD) integration with the following content and replacing the placeholders with actual values.
{
"client_id": "${your_client_id}",
"client_secret": "${your_client_secret}",
"jwt_payload": {
"exp": ${your_expiration_time},
"iss": "${your_org@AdobeOrg}",
"sub": "${your_tech_id@techacct.adobe.com}",
"https://ims-na1.adobelogin.com/s/ent_dataservices_sdk": true,
"aud": "https://ims-na1.adobelogin.com/c/${your_client_id}"
},
"token_exchange_url": "https://ims-na1.adobelogin.com/ims/exchange/jwt/",
"jwt_private_key": "${path to your private.key file used in Adobe I/O integration}",
"x-sandbox-id": "${your_sandbox_id}",
"x-sandbox-name": "${your_sandbox_name}",
"env": "prod"
}
- Run the following commands now (in the particular order): `
$ aio config:set jwt-auth ${path_to_the_above_config.json} --file --json
$ aio jwt-auth:access-token
- Mount the 'aio' file under your root .config director (~/.config/aio) and make docker container aware of it
$ docker run -it --rm -v ~/.config:/root/.config --entrypoint /bin/bash aio-cli-plugin-aep -s
- Test: $ aio aep:datasets:list
Note: In order to regenerate the access_token (in case of 403 status code), stop the container and rerun step# 4, 5 and 6.
6. (Developers) To run unit tests from the root folder of the project run the commands in following order
$ npm install
$ jest
$ jest --coverage (to see coverage report)