README
license-auditor
License Auditor helps you track and validate licenses inside your project.
License Auditor helps you track and validate licenses inside your project. Prevents unwanted law complications. The license Auditor includes a step in your pipeline and creates notifications about potential problems with used licenses. At the moment, a notification means a comment.
Getting started
To start using the License Auditor, install its package with NPM:
npm install @brainhubeu/license-auditor
or Yarn:
yarn add @brainhubeu/license-auditor
In the next step, copy license directory with licenses.js, blacklist.js, and whitelist.js files. The first one contains a full list of all currently acknowledged, depreciated, and exceptional software licenses. To whitelist or blacklist the license, you must copy selected licenses from the main file into them.
Whitelisting stops License Auditor from analyzing and displaying any notifications for a given package with whitelisted license type. Blacklisting a license leads to the generation of fail notification log or causes CI job to fail if the blacklisted license is found, which prevents the developer from merging unwanted dependencies into the destination branch. Any license that is included in neither blacklist.js nor whitelist.js, but is found during packages analyze or merge request, becomes a warning, which developer should address during merge process or further development.
If a given dependency has no license specified, it's marked with UNKNOWN and thus the default blacklist contains UNKNOWN license to notify about a potentially unwanted license.
For License Auditor to work, all project dependencies have to be installed before an audit. License Auditor iterates through the node_modules and retrieves the license information from them. List of licenses is also available at spdx site.
The order of files in which the license information is retrieved from is: package.json, LICENSE, LICENCE, COPYING, README. Warning and Error notifications specify the license file that it has been read from. In some cases, license files may not provide the license directly. The asterisk * symbol next to shown license name indicates that it is the closest possible, but not fully confirmed license.
Usage and examples
Continuous Integration tools adaptation
If you intend to use License Auditor with GitLab CI or GitHub Actions, you have to copy CI example file to the root of your project directory and RENAME it to dangerfile.js. This example provides a base for CI-oriented licenses checking using DangerJS (for more information this framework, visit official Danger Systems site).
Then, you have to include it in your pipeline. The basic structure of Gitlab pipeline step should look like this:
check_foo_licenses:
stage: CheckFooLicenses
image: node:alpine
script:
- yarn add -D danger @brainhubeu/license-auditor
- yarn danger ci --failOnErrors --id Foo
variables:
DANGER_GITLAB_API_TOKEN: $GITLAB_ACCESS_TOKEN
PROJECT_PATH: $PATH_TO_FOO_PACKAGE # it could look like: ./packages/web or ./server
only:
- merge_requests
and the basic structure for Github Actions:
- name: CheckBarLicenses
run: |
yarn add -D danger @brainhubeu/license-auditor
yarn danger ci --failOnErrors --verbose --id Bar
env:
DANGER_GITHUB_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_ACCESS_TOKEN }}
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
PROJECT_PATH: $PATH_TO_BAR_PACKAGE # it could look like: ./packages/web or ./server
You can find more examples in examples directory for GitLab and GitHub.
To allow automatic comments posting on MRs/PRs, you need to create either Gitlab Access Token or Github Access Token in a profile that is going to post comments
under MRs/ PRs. Then you need to specify environmental variables with key DANGER_GITLAB_API_TOKEN or DANGER_GITHUB_API_TOKEN and value being the acquired token.
The Access Token needs to have the ability to use the Github/Gitlab API and write discussions for MRs/PRs.
Gitlab:
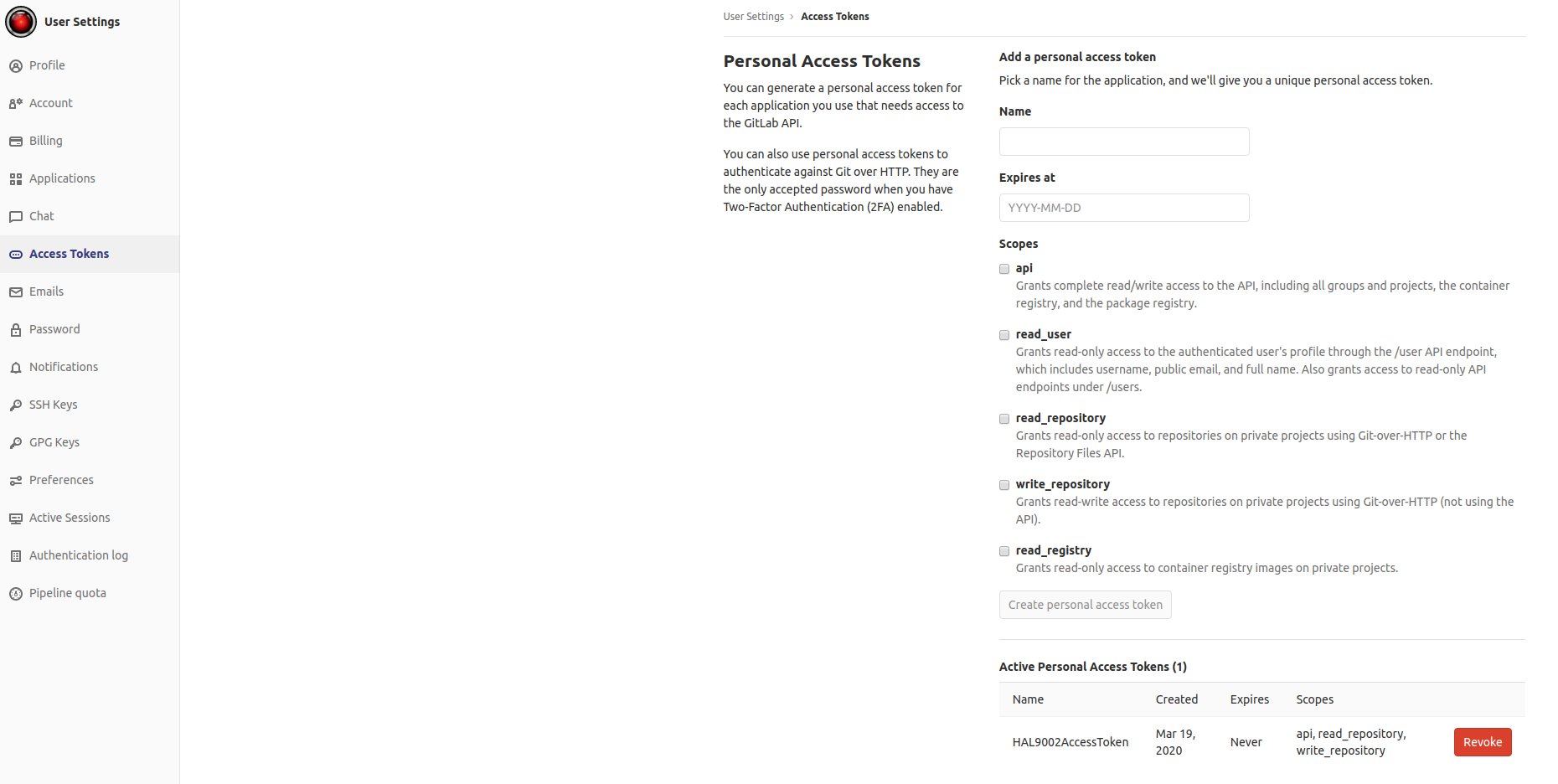
Github:
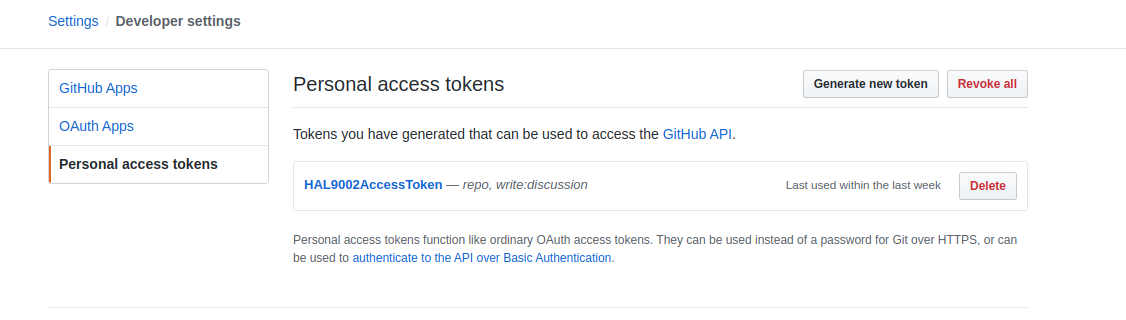
In provided examples, the new Gitlab and Github accounts were created to act as a "bot", that was posting MR/PR comments based on license information. Both of them were named HAL9002.
The comments should look similar to:
for Gitlab:
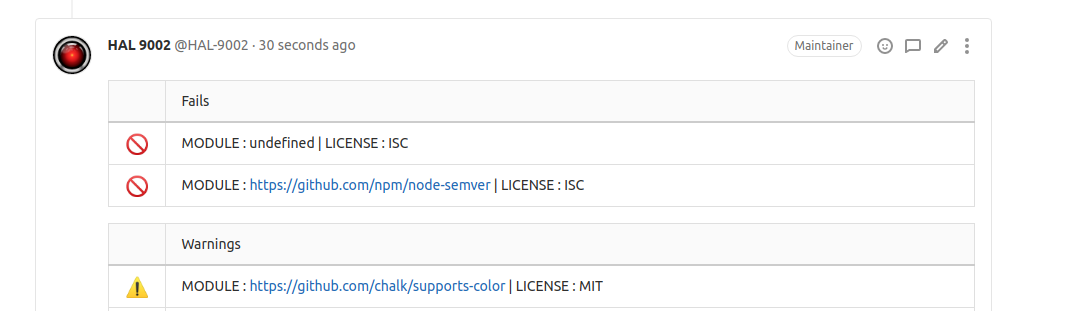
for Github:
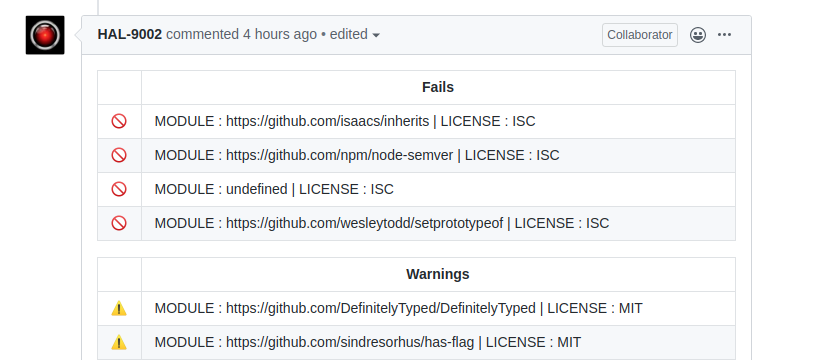
You can find more information about Github and Gitlab configuration here.
Logging tool and own implementation
To use a logging tool instead of CI, copy logging example file to the root of your project directory. It is intended to log used license information into the console of your preference. To use it, you need to have a JavaScript runtime environment installed (e.g. Node.js). Then, just simply type:
node logging_example.js
This command will list fails for every dependency that was blacklisted in blacklist.js file and warnings for licenses that are missing on both whitelist.js and blacklist.js files.
You can also create your own implementation of warn and fail methods behavior based on your needs. To do so, we recommend to copy logging example file and change fail and warn methods implementations, remembering to preserve msg input parameter and not to add new parameters, as they will be of no use.
Contributing
Releasing a new version of the package
- Create a new branch
release-<version>e.g.release-v1.1.1. - Run
yarn versioncommand and set a new version e.gv1.1.1. Follow Semantic Versioning 2.0.0. - Push your branch along with created tag e.g.
git push --set-upstream origin release-v1.1.1 --tags. - Open pull request.
- Once pull request is merged, create a new release on Github. Select existing tag e.g.
v1.1.1and fill in release notes. A new version will be published using Github Actions :tada:.
Tests
- run
yarn test
About
license-auditor was built using:
license-auditor is maintained by @jkthomas, @nikodemwrona and the Brainhub development team. It is funded by Brainhub and the names and logos for Brainhub are trademarks of Brainhub Sp. z o.o.. You can check other open-source projects supported/developed by our teammates here.
We love open-source JavaScript software! See our other projects or hire us to build your next web, desktop, and mobile application with JavaScript.









