README
react-native-heat-map
A <View/>s with transparency. If you don't feel like using a native library, you might be interested in react-native-simpleheat.
| Android | iOS |
|---|---|
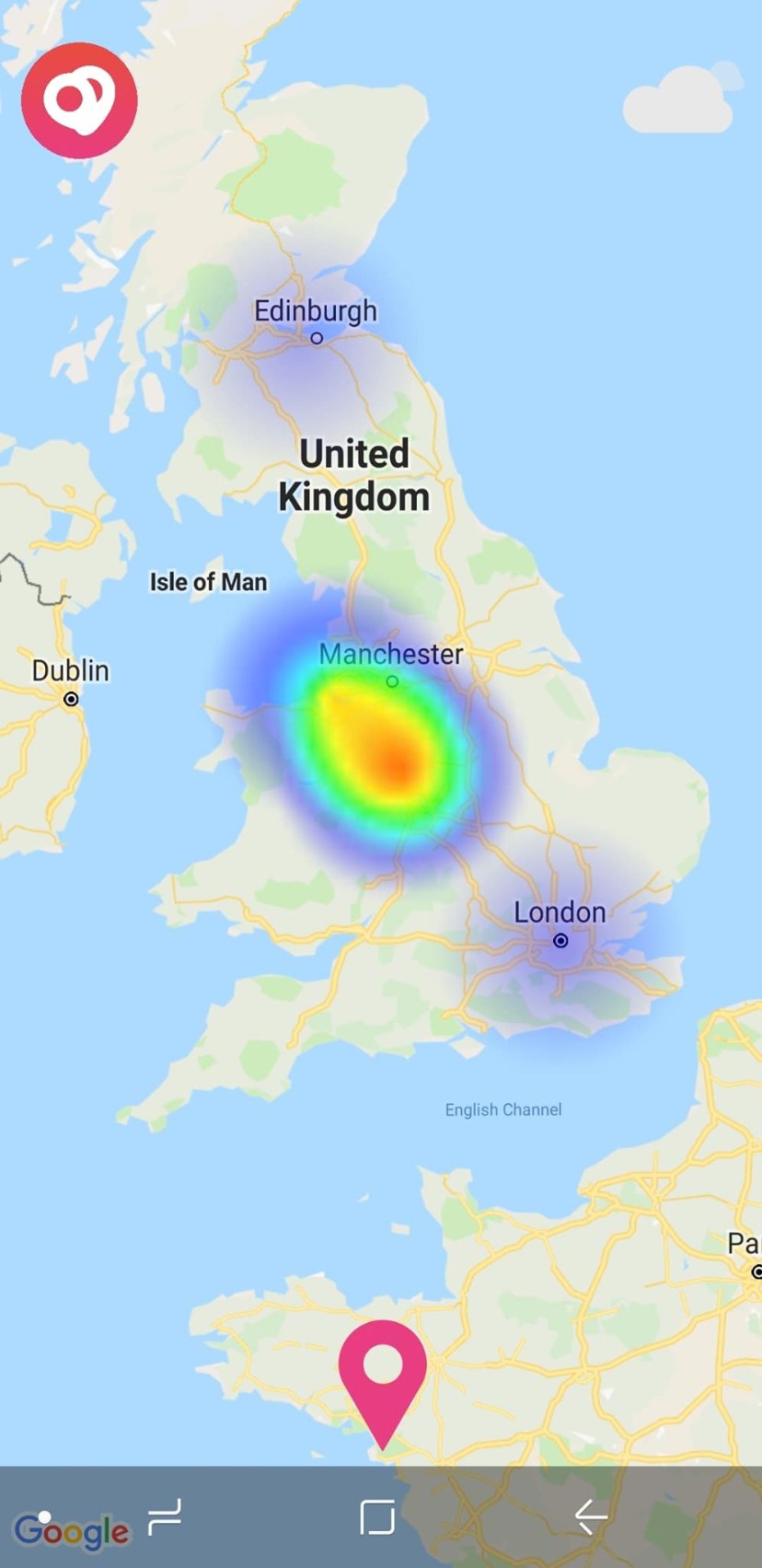 |
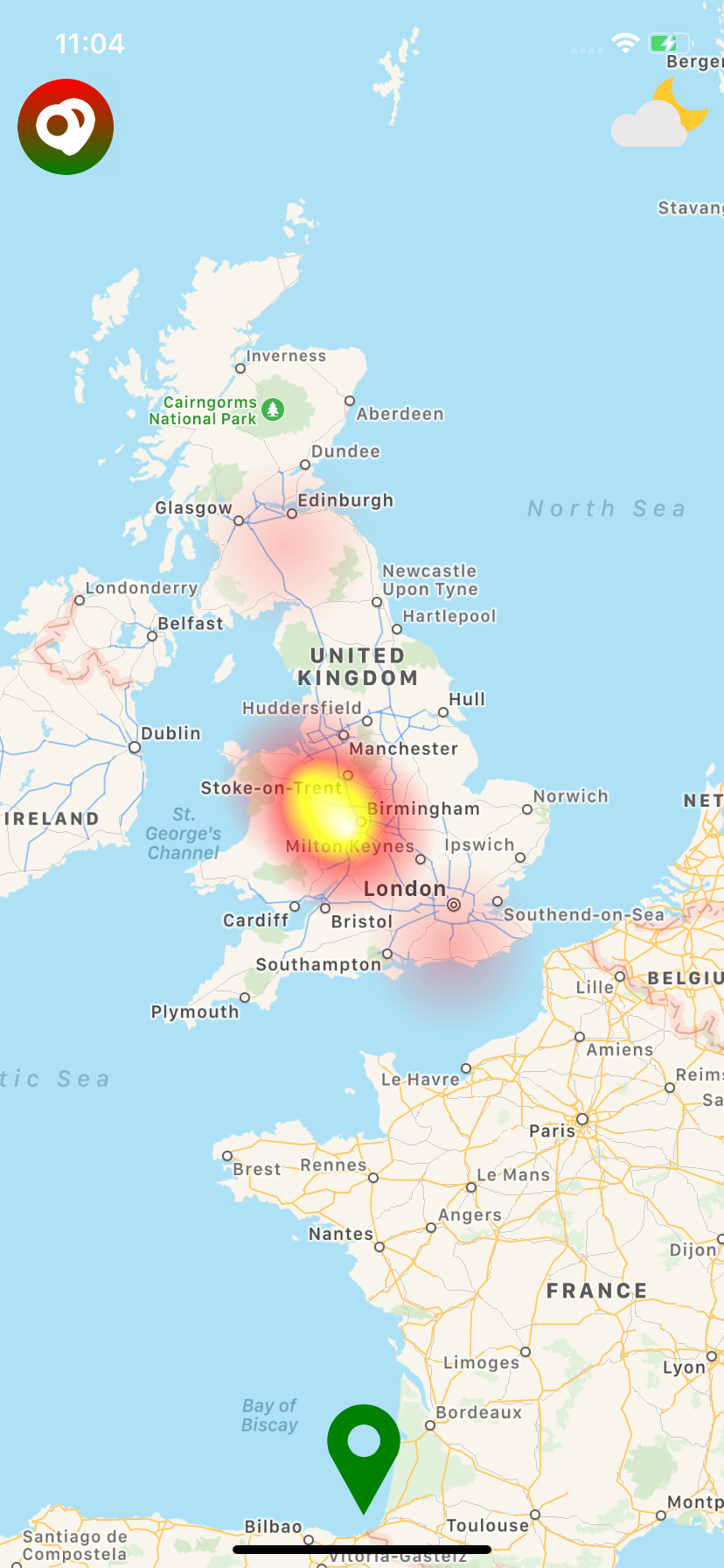 |
The native Android solution is implemented using simpleheat as the development reference. On iOS, the heatmap is presented using the performant LFHeatMap as a CocoaPods dependeny. This is not a <MapView/>; but it can be overlaid one.
🚀 Getting started
Using npm:
$ npm install @cawfree/react-native-heat-map --save
Using yarn:
yarn add @cawfree/react-native-heat-map
🤖 Mostly automatic installation
If you're running react-native at any version less than 0.60.0, you'll need to manually link the library to your project:
$ react-native link react-native-heat-map
🔩 Manual installation
iOS
- In XCode, in the project navigator, right click
Libraries➜Add Files to [your project's name] - Go to
node_modules➜react-native-heat-mapand addHeatMap.xcodeproj - In XCode, in the project navigator, select your project. Add
libHeatMap.ato your project'sBuild Phases➜Link Binary With Libraries - Run your project (
Cmd+R)<
Android
- Open up
android/app/src/main/java/[...]/MainApplication.java
- Add
import io.github.cawfree.HeatMapPackage;to the imports at the top of the file - Add
new HeatMapPackage()to the list returned by thegetPackages()method
- Append the following lines to
android/settings.gradle:include ':react-native-heat-map' project(':react-native-heat-map').projectDir = new File(rootProject.projectDir, '../node_modules/react-native-heat-map/android') - Insert the following lines inside the dependencies block in
android/app/build.gradle:compile project(':react-native-heat-map')
✍️ Example
There are two main modes the <HeatMap/> can operate in. You can either specify cartesian (2D) co-ordinates:
import HeatMap from 'react-native-heat-map';
export default () => (
<HeatMap
pointerEvents="box-only"
style={{
flex: 1,
}}
data={[
[
100, // x
100, // y
20 // intensity
],
]}
/>
);
Alternatively, you can pass a react-native-maps-compatible region prop to process your data through a Web Mercator Projection:
import HeatMap from 'react-native-heat-map';
export default () => (
<HeatMap
pointerEvents="box-only"
style={{
flex: 1,
}}
data={[
[
-3.0118499, // longitude
53.4139281, // latitude
20 // intensity
],
]}
region={{
longitude: -3.0118499,
latitude: 53.4139281,
latitudeDelta: 0.2,
longitudeDelta: 0.2,
}}
/>
);
For performance, instead of using setState to update the <HeatMap />, you can choose to setNativeProps directly.
Check out the complete example code.
📌 Props
| Prop | Type | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| max | number | 10 | No |
| data | array | [] | No |
| minOpacity | number | 0.05 | No |
| alpha | number | 1.0 | No |
| region | shape | null | No |