README
Interactive Image Registration for JupyterLab
Rej can be used to achieve registration between two images, probably GeoTIFFs, but any format rasterio can read should work fine.
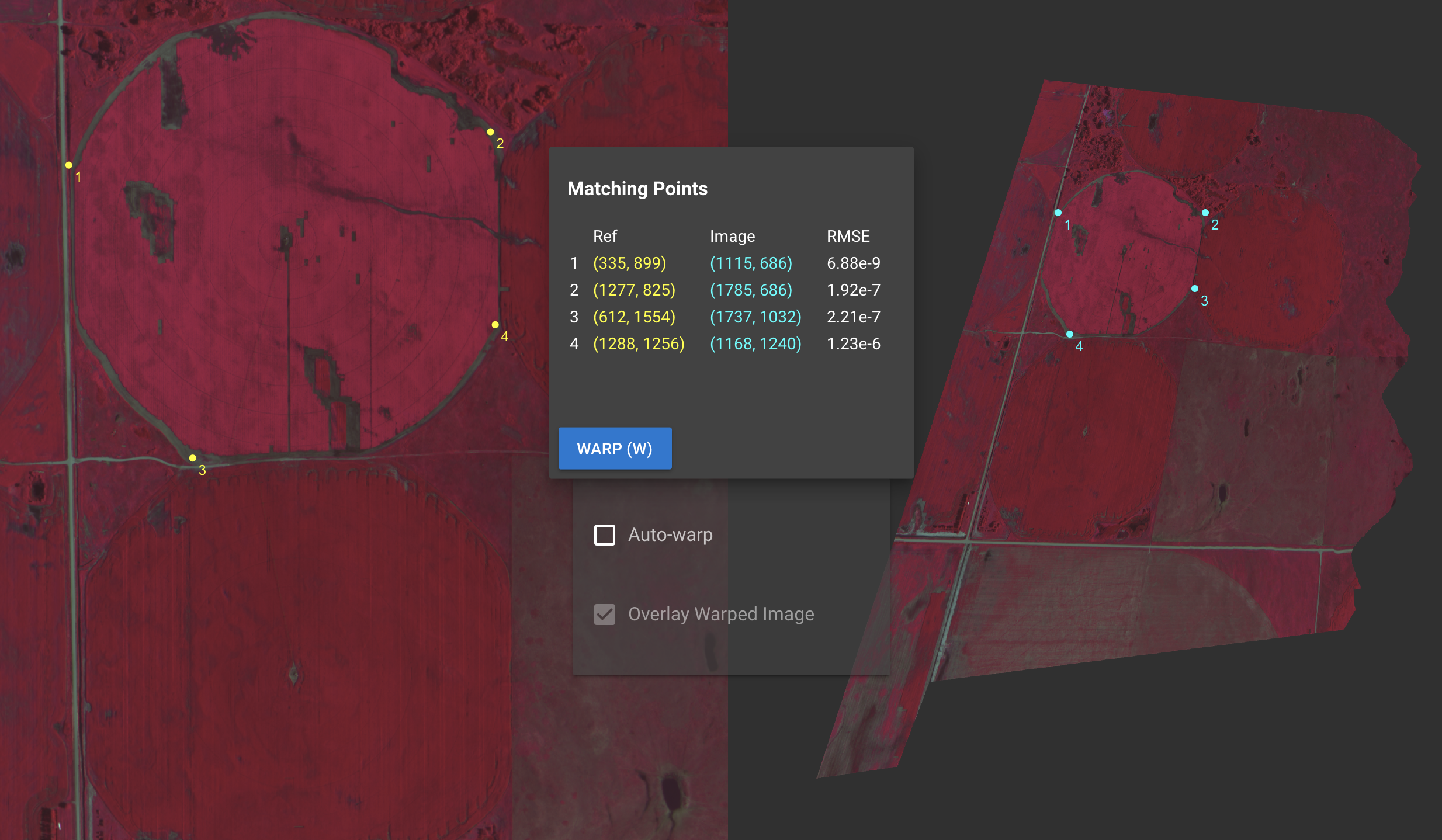
Registration is achieved by selecting reference ("ground control") points on both
images. A .PTS file is output containing pixel coordinates of corresponding points.
Eventually, a new GeoTIFF can be output, we're working on it 🤙🏽.
Installing Rej
You'll need both the JupyterLab widget, as well as the python library:
jupyter labextension install @ceresimaging/rej
pip install rej
Using Rej
import rej
rej.register('./file1.tiff', './file2.tiff')
This should bring up the interactive UI shown above inside your jupyter notebook. Clicking "Save" will output a PTS file, which may be applied to the images to transform them. Enjoy!
Effective Rej Development
Most of Rej is written in Javascript/VueJS, which is then accessed through a thin python library. Development will mostly take place inside the context of JupyterLab, so its nice to set things up so every time you save a file, the JupyterLab extension is updated:
pip install -r requirements.txt && pip install -e . && jupyter nbextension enable --py widgetsnbextension && jupyter labextension install --no-build @jupyter-widgets/jupyterlab-manager && npm install- In one terminal:
npm run watch - In another terminal:
npm run jupyterlab
Run outside JupyterLab for faster dev iteration
If you're working on a feature/bug that doesn't require jupyterlab, you may prefer to develop inside Vue CLI's hot-reloading app mode. To do this:
npm run serve
Publish an updated version to pypi & npm (this will also update the ICIN build)
- Increment "version" in
package.json npm run installnpm run buildnpm run publish:all