README
electron-shared-state
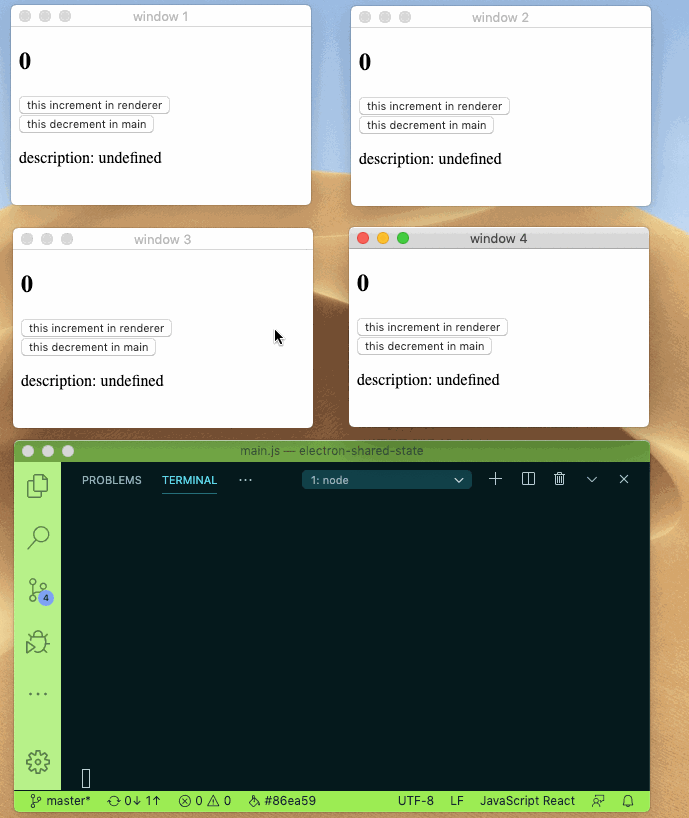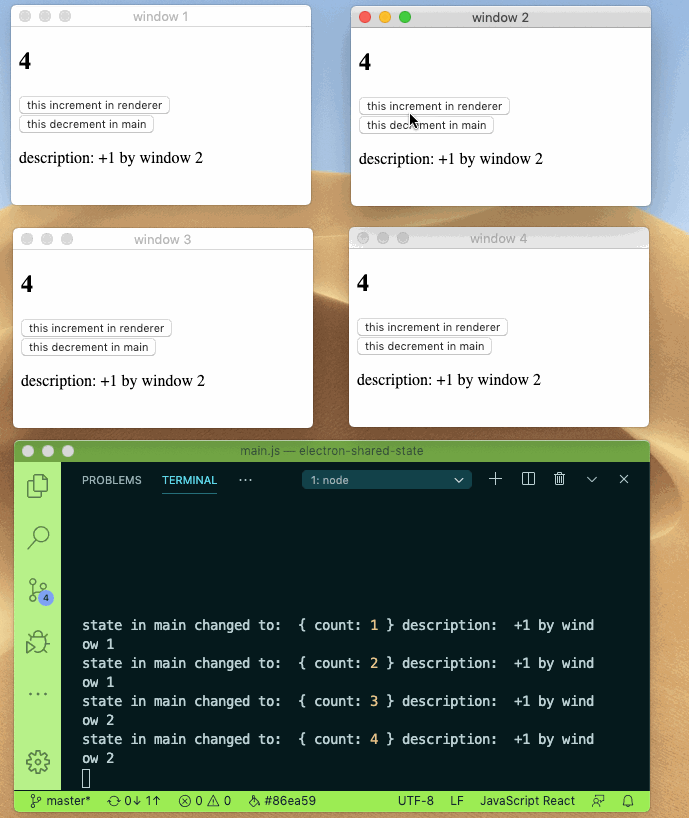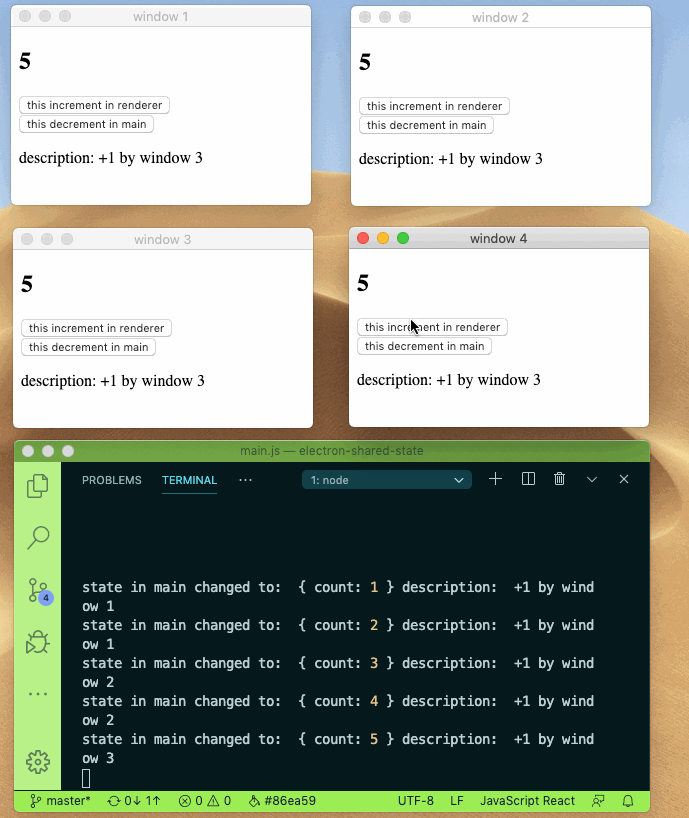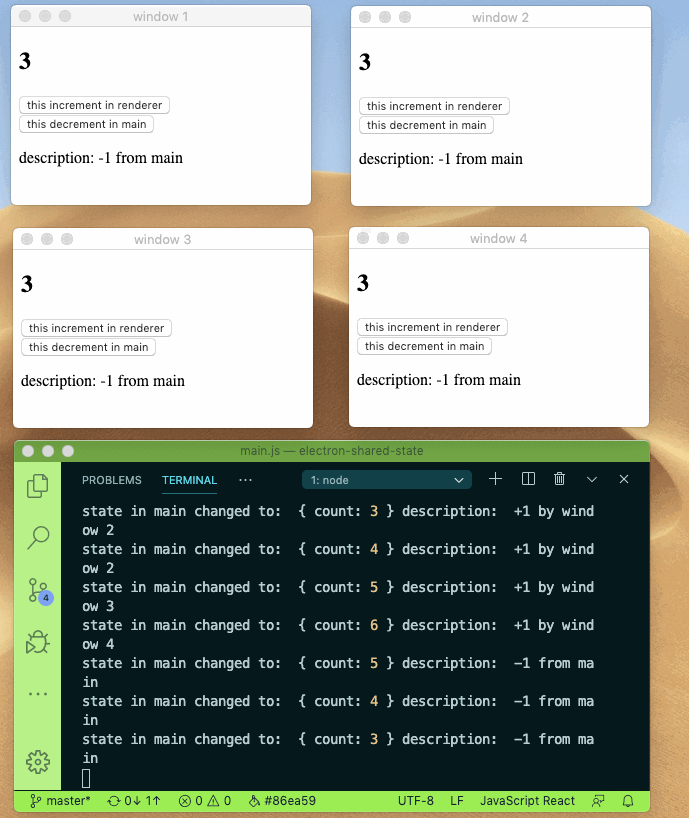
Sharing state between main and renderer process can be this easy.
- 🚀 Mutate your state while keep them in sync with other process
- 🎯 Write in typescript with full typing support
- ❤️ Elegant and easy to learn API
- 👻 Immutability and structural sharing out of the box with built-in immer
Install
npm install electron-shared-state
or
yarn add electron-shared-state
Usage
// shared
export const initialState = 0;
// renderer
import { createSharedStore } from 'electron-shared-state';
const sharedStore = createSharedStore(initialState);
sharedStore.subscribe((state) => {
console.log(state);
});
setTimeout(() => {
sharedStore.setState((state) => {
state = state + 1;
});
}, 2000);
// main
import { createSharedStore } from 'electron-shared-state';
const sharedStore = createSharedStore(initialState);
sharedStore.subscribe((state) => {
console.log(state);
});
// both main and renderer will print the state after two seconds.
check source code under example directory for more info.
API Reference
electron-shared-state only provides one simple function: createSharedStore. The signature is like below:
function createSharedStore<T>(state: T): {
setState: (recipe: (draft: T) => void, description?: string | undefined) => T;
getState: () => T;
subscribe: (
listener: (state: T, description?: string | undefined) => void
) => () => void;
};
The input is the state your want to share across processes, generally it's an object.
It returns a Store object with a few methods on it.
setState(stateUpdater, description)
Accepts a stateUpdater function and a description string for debug purpose. The stateUpdater is like the second argument of immer's produce, so it inherits immer's pitfalls.
Returns the new state. It use immer underneath so the state remains immutable, to keep it in sync across processes, you should always use setState to update it.
getState()
Returns the current state.
subscribe(listener)
Adds a change listener. It will be called any time the state is changed, the listener receives the latest state and a description string as arguments.
