README
json2csv
Converts json into csv with column titles and proper line endings.
Can be used as a module and from the command line.
See the CHANGELOG for details about the latest release.
Features
- Fast and lightweight
- Scalable to infinitely large datasets (using stream processing)
- Support for standard JSON as well as NDJSON
- Advanced data selection (automatic field discovery, underscore-like selectors, custom data getters, default values for missing fields, transforms, etc.)
- Highly customizable (supportting custom quotation marks, delimiters, eol values, etc.)
- Automatic escaping (preserving new lines, quotes, etc. in them)
- Optional headers
- Unicode encoding support
- Pretty printing in table format to stdout
How to install
You can install json2csv as a dependency using NPM.
Requires Node v10 or higher.
# Global so it can be called from anywhere
$ npm install -g json2csv
# or as a dependency of a project
$ npm install json2csv --save
Also, if you are loading json2csv directly to the browser you can pull it directly from the CDN.
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/json2csv"></script>
By default, the above script will get the latest release of json2csv. You can also specify a specific version:
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/json2csv@4.2.1"></script>
Command Line Interface
json2csv can be called from the command line if installed globally (using the -g flag).
Usage: json2csv [options]
Options:
-V, --version output the version number
-i, --input <input> Path and name of the incoming json file. Defaults to stdin.
-o, --output <output> Path and name of the resulting csv file. Defaults to stdout.
-c, --config <path> Specify a file with a valid JSON configuration.
-n, --ndjson Treat the input as NewLine-Delimited JSON.
-s, --no-streaming Process the whole JSON array in memory instead of doing it line by line.
-f, --fields <fields> List of fields to process. Defaults to field auto-detection.
-v, --default-value <defaultValue> Default value to use for missing fields.
-q, --quote <quote> Character(s) to use as quote mark. Defaults to '"'.
-Q, --escaped-quote <escapedQuote> Character(s) to use as a escaped quote. Defaults to a double `quote`, '""'.
-d, --delimiter <delimiter> Character(s) to use as delimiter. Defaults to ','. (default: ",")
-e, --eol <eol> Character(s) to use as End-of-Line for separating rows. Defaults to '\n'. (default: "\n")
-E, --excel-strings Wraps string data to force Excel to interpret it as string even if it contains a number.
-H, --no-header Disable the column name header.
-a, --include-empty-rows Includes empty rows in the resulting CSV output.
-b, --with-bom Includes BOM character at the beginning of the CSV.
-p, --pretty Print output as a pretty table. Use only when printing to console.
--unwind [paths] Creates multiple rows from a single JSON document similar to MongoDB unwind.
--unwind-blank When unwinding, blank out instead of repeating data. Defaults to false. (default: false)
--flatten-objects Flatten nested objects. Defaults to false. (default: false)
--flatten-arrays Flatten nested arrays. Defaults to false. (default: false)
--flatten-separator <separator> Flattened keys separator. Defaults to '.'. (default: ".")
-h, --help output usage information
If no input -i is specified the result is expected from to the console standard input.
If no output -o is specified the result is printed to the console standard output.
If no fields -f or config -c are passed the fields of the first element are used since json2csv CLI process the items one at a time. You can use the --no-streaming flag to load the entire JSON in memory and get all the headers. However, keep in mind that this is slower and requires much more memory.
Use -p to show the result as a table in the console.
Any option passed through the config file -c will be overriden if a specific flag is passed as well. For example, the fields option of the config will be overriden if the fields flag -f is used.
CLI examples
All examples use this example input file.
Input file and specify fields
$ json2csv -i input.json -f carModel,price,color
carModel,price,color
"Audi",10000,"blue"
"BMW",15000,"red"
"Mercedes",20000,"yellow"
"Porsche",30000,"green"
Input file, specify fields and use pretty logging
$ json2csv -i input.json -f carModel,price,color -p
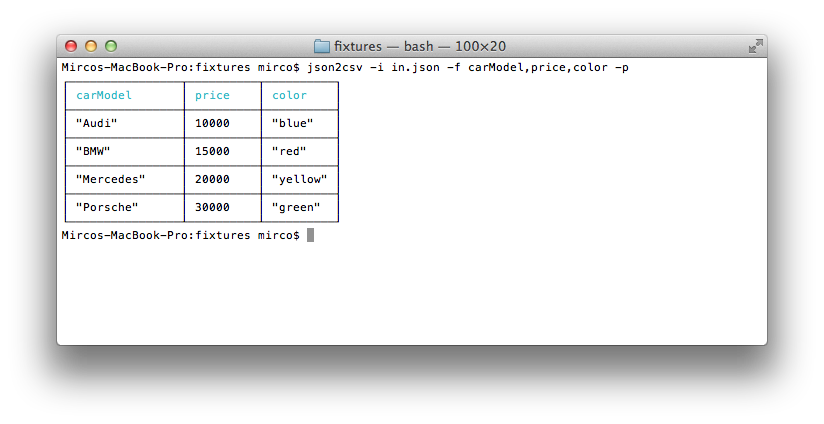
Generating CSV containing only specific fields
$ json2csv -i input.json -f carModel,price,color -o out.csv
$ cat out.csv
carModel,price,color
"Audi",10000,"blue"
"BMW",15000,"red"
"Mercedes",20000,"yellow"
"Porsche",30000,"green"
Same result will be obtained passing the fields config as a file.
$ json2csv -i input.json -c fieldsConfig.json -o out.csv
where the file fieldsConfig.json contains
[
"carModel",
"price",
"color"
]
Read input from stdin
$ json2csv -f price
[{"price":1000},{"price":2000}]
Hit Enter and afterwards CTRL + D to end reading from stdin. The terminal should show
price
1000
2000
Appending to existing CSV
Sometimes you want to add some additional rows with the same columns. This is how you can do that.
# Initial creation of csv with headings
$ json2csv -i test.json -f name,version > test.csv
# Append additional rows
$ json2csv -i test.json -f name,version --no-header >> test.csv
Javascript module
json2csv can also be use programatically from you javascript codebase.
Available Options
The programatic APIs take a configuration object very equivalent to the CLI options.
fields- Array of Objects/Strings. Defaults to toplevel JSON attributes. See example below.ndjson- Only effective on the streaming API. Indicates that data coming through the stream is NDJSON.transforms- Array of transforms to be applied to each data item. A transform is simply a function that receives a data item and returns the transformed item.defaultValue- String, default value to use when missing data. Defaults to<empty>if not specified. (Overridden byfields[].default)quote- String, quote around cell values and column names. Defaults to"if not specified.escapedQuote- String, the value to replace escaped quotes in strings. Defaults to 2xquotes(for example"") if not specified.delimiter- String, delimiter of columns. Defaults to,if not specified.eol- String, overrides the default OS line ending (i.e.\non Unix and\r\non Windows).excelStrings- Boolean, converts string data into normalized Excel style data.header- Boolean, determines whether or not CSV file will contain a title column. Defaults totrueif not specified.includeEmptyRows- Boolean, includes empty rows. Defaults tofalse.withBOM- Boolean, with BOM character. Defaults tofalse.
json2csv parser (Synchronous API)
json2csv can also be used programatically as a synchronous converter using its parse method.
const { Parser } = require('json2csv');
const fields = ['field1', 'field2', 'field3'];
const opts = { fields };
try {
const parser = new Parser(opts);
const csv = parser.parse(myData);
console.log(csv);
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
}
you can also use the convenience method parse
const { parse } = require('json2csv');
const fields = ['field1', 'field2', 'field3'];
const opts = { fields };
try {
const csv = parse(myData, opts);
console.log(csv);
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
}
Both of the methods above load the entire JSON in memory and do the whole processing in-memory while blocking Javascript event loop. For that reason is rarely a good reason to use it until your data is very small or your application doesn't do anything else.
json2csv async parser (Streaming API)
The synchronous API has the downside of loading the entire JSON array in memory and blocking javascript's event loop while processing the data. This means that your server won't be able to process more request or your UI will become irresponsive while data is being processed. For those reasons, is rarely a good reason to use it unless your data is very small or your application doesn't do anything else.
The async parser process the data as a non-blocking stream. This approach ensures a consistent memory footprint and avoid blocking javascript's event loop. Thus, it's better suited for large datasets or system with high concurrency.
One very important difference between the asynchronous and the synchronous APIs is that using the asynchronous API json objects are processed one by one. In practice, this means that only the fields in the first object of the array are automatically detected and other fields are just ignored. To avoid this, it's advisable to ensure that all the objects contain exactly the same fields or provide the list of fields using the fields option.
The async API uses takes a second options arguments that's directly passed to the underlying streams and accept the same options as the standard Node.js streams.
Instances of AsyncParser expose three objects:
- input: Which allows to push more data
- processor: A readable string representing the whole data processing. You can listen to all the standard events of Node.js streams.
- transform: The json2csv transform. See bellow for more details.
const { AsyncParser } = require('json2csv');
const fields = ['field1', 'field2', 'field3'];
const opts = { fields };
const transformOpts = { highWaterMark: 8192 };
const asyncParser = new AsyncParser(opts, transformOpts);
let csv = '';
asyncParser.processor
.on('data', chunk => (csv += chunk.toString()))
.on('end', () => console.log(csv))
.on('error', err => console.error(err));
// You can also listen for events on the conversion and see how the header or the lines are coming out.
asyncParser.transform
.on('header', header => console.log(header))
.on('line', line => console.log(line))
.on('error', err => console.log(err));
asyncParser.input.push(data); // This data might come from an HTTP request, etc.
asyncParser.input.push(null); // Sending `null` to a stream signal that no more data is expected and ends it.
AsyncParser also exposes some convenience methods:
fromInputallows you to set the input stream.throughTransformallows you to add transforms to the stream.toOutputallows you to set the output stream.promisereturns a promise that resolves when the stream ends or errors. Takes a boolean parameter to indicate if the resulting CSV should be kept in-memory and be resolved by the promise.
const { createReadStream, createWriteStream } = require('fs');
const { AsyncParser } = require('json2csv');
const fields = ['field1', 'field2', 'field3'];
const opts = { fields };
const transformOpts = { highWaterMark: 8192 };
// Using the promise API
const input = createReadStream(inputPath, { encoding: 'utf8' });
const asyncParser = new JSON2CSVAsyncParser(opts, transformOpts);
const parsingProcessor = asyncParser.fromInput(input);
parsingProcessor.promise()
.then(csv => console.log(csv))
.catch(err => console.error(err));
// Using the promise API just to know when the process finnish
// but not actually load the CSV in memory
const input = createReadStream(inputPath, { encoding: 'utf8' });
const output = createWriteStream(outputPath, { encoding: 'utf8' });
const asyncParser = new JSON2CSVAsyncParser(opts, transformOpts);
const parsingProcessor = asyncParser.fromInput(input).toOutput(output);
parsingProcessor.promise(false).catch(err => console.error(err));
you can also use the convenience method parseAsync which accept both JSON arrays/objects and readable streams and returns a promise.
const { parseAsync } = require('json2csv');
const fields = ['field1', 'field2', 'field3'];
const opts = { fields };
parseAsync(myData, opts)
.then(csv => console.log(csv))
.catch(err => console.error(err));
json2csv transform (Streaming API)
json2csv also exposes the raw stream transform so you can pipe your json content into it. This is the same Transform that AsyncParser uses under the hood.
const { createReadStream, createWriteStream } = require('fs');
const { Transform } = require('json2csv');
const fields = ['field1', 'field2', 'field3'];
const opts = { fields };
const transformOpts = { highWaterMark: 16384, encoding: 'utf-8' };
const input = createReadStream(inputPath, { encoding: 'utf8' });
const output = createWriteStream(outputPath, { encoding: 'utf8' });
const json2csv = new Transform(opts, transformOpts);
const processor = input.pipe(json2csv).pipe(output);
// You can also listen for events on the conversion and see how the header or the lines are coming out.
json2csv
.on('header', header => console.log(header))
.on('line', line => console.log(line))
.on('error', err => console.log(err));
The stream API can also work on object mode. This is useful when you have an input stream in object mode or if you are getting JSON objects one by one and want to convert them to CSV as they come.
const { Transform } = require("json2csv");
const { Readable } = require('stream');
const input = new Readable({ objectMode: true });
input._read = () => {};
// myObjectEmitter is just a fake example representing anything that emit objects.
myObjectEmitter.on('object', obj => input.push(obj));
// Pushing a null close the stream
myObjectEmitter.end(() => input.push(null));
const output = process.stdout;
const opts = {};
const transformOpts = { objectMode: true };
const json2csv = new Transform(opts, transformOpts);
const processor = input.pipe(json2csv).pipe(output);
Data transforms
json2csv supports data transforms. A transform is simply a function that receives a data item and returns the transformed item.
Custom transforms
function (item) {
// apply tranformations or create new object
return transformedItem;
}
or using ES6
(item) => {
// apply tranformations or create new object
return transformedItem;
}
For example, let's add a line counter to our CSV, capitalize the car field and change the price to be in Ks (1000s).
let counter = 1;
(item) => ({ counter: counter++, ...item, car: item.car.toUpperCase(), price: item.price / 1000 });
Built-in transforms
There is a number of built-in transform provider by the library.
const { transforms: { unwind, flatten } } = require('json2csv');
Unwind
The unwind transform deconstructs an array field from the input item to output a row for each element. Is's similar to MongoDB's $unwind aggregation.
The transform needs to be instantiated and takes an options object as arguments containing:
paths- Array of String, list the paths to the fields to be unwound. It's mandatory and should not be empty.blankOut- Boolean, unwind using blank values instead of repeating data. Defaults tofalse.
// Default
unwind({ paths: ['fieldToUnwind'] });
// Blanking out repeated data
unwind({ paths: ['fieldToUnwind'], blankOut: true });
Flatten
Flatten nested javascript objects into a single level object.
The transform needs to be instantiated and takes an options object as arguments containing:
objects- Boolean, whether to flatten JSON objects or not. Defaults totrue.arrays- Boolean, whether to flatten Arrays or not. Defaults tofalse.separator- String, separator to use between nested JSON keys when flattening a field. Defaults to..
// Default
flatten();
// Custom separator '__'
flatten({ separator: '_' });
// Flatten only arrays
flatten({ objects: false, arrays: true });
Javascript module examples
Example fields option
{
fields: [
// Supports pathname -> pathvalue
'simplepath', // equivalent to {value:'simplepath'}
'path.to.value' // also equivalent to {value:'path.to.value'}
// Supports label -> simple path
{
label: 'some label', // Optional, column will be labeled 'path.to.something' if not defined)
value: 'path.to.something', // data.path.to.something
default: 'NULL' // default if value is not found (Optional, overrides `defaultValue` for column)
},
// Supports label -> derived value
{
label: 'some label', // Optional, column will be labeled with the function name or empty if the function is anonymous
value: (row, field) => row[field.label].toLowerCase() ||field.default,
default: 'NULL' // default if value function returns null or undefined
},
// Supports label -> derived value
{
value: (row) => row.arrayField.join(',')
},
// Supports label -> derived value
{
value: (row) => `"${row.arrayField.join(',')}"`
},
]
}
Example 1
const { Parser } = require('json2csv');
const myCars = [
{
"car": "Audi",
"price": 40000,
"color": "blue"
}, {
"car": "BMW",
"price": 35000,
"color": "black"
}, {
"car": "Porsche",
"price": 60000,
"color": "green"
}
];
const json2csvParser = new Parser();
const csv = json2csvParser.parse(myCars);
console.log(csv);
will output to console
"car", "price", "color"
"Audi", 40000, "blue"
"BMW", 35000, "black"
"Porsche", 60000, "green"
Example 2
You can choose which fields to include in the CSV.
const { Parser } = require('json2csv');
const fields = ['car', 'color'];
const json2csvParser = new Parser({ fields });
const csv = json2csvParser.parse(myCars);
console.log(csv);
will output to console
"car", "color"
"Audi", "blue"
"BMW", "black"
"Porsche", "green"
Example 3
You can choose custom column names for the exported file.
const { Parser } = require('json2csv');
const fields = [{
label: 'Car Name',
value: 'car'
},{
label: 'Price USD',
value: 'price'
}];
const json2csvParser = new Parser({ fields });
const csv = json2csvParser.parse(myCars);
console.log(csv);
will output to console
"Car Name", "Price USD"
"Audi", 40000
"BMW", 35000
"Porsche", 60000
Example 4
You can also specify nested properties using dot notation.
const { Parser } = require('json2csv');
const myCars = [
{
"car": { "make": "Audi", "model": "A3" },
"price": 40000,
"color": "blue"
}, {
"car": { "make": "BMW", "model": "F20" },
"price": 35000,
"color": "black"
}, {
"car": { "make": "Porsche", "model": "9PA AF1" },
"price": 60000,
"color": "green"
}
];
const fields = ['car.make', 'car.model', 'price', 'color'];
const json2csvParser = new Parser({ fields });
const csv = json2csvParser.parse(myCars);
console.log(csv);
will output to console
"car.make", "car.model", "price", "color"
"Audi", "A3", 40000, "blue"
"BMW", "F20", 35000, "black"
"Porsche", "9PA AF1", 60000, "green"
Example 5
Use a custom delimiter to create tsv files using the delimiter option:
const { Parser } = require('json2csv');
const json2csvParser = new Parser({ delimiter: '\t' });
const tsv = json2csvParser.parse(myCars);
console.log(tsv);
will output to console
"car" "price" "color"
"Audi" 10000 "blue"
"BMW" 15000 "red"
"Mercedes" 20000 "yellow"
"Porsche" 30000 "green"
If no delimiter is specified, the default , is used.
Example 6
You can choose custom quotation marks.
const { Parser } = require('json2csv');
const json2csvParser = new Parser({ quote: '' });
const csv = json2csvParser.parse(myCars);
console.log(csv);
will output to console
car, price, color
Audi, 40000, blue
BMW", 35000, black
Porsche", 60000, green
Example 7
You can unwind arrays similar to MongoDB's $unwind operation using the unwind transform.
const { Parser, transforms: { unwind } } = require('json2csv');
const myCars = [
{
"carModel": "Audi",
"price": 0,
"colors": ["blue","green","yellow"]
}, {
"carModel": "BMW",
"price": 15000,
"colors": ["red","blue"]
}, {
"carModel": "Mercedes",
"price": 20000,
"colors": "yellow"
}, {
"carModel": "Porsche",
"price": 30000,
"colors": ["green","teal","aqua"]
}
];
const fields = ['carModel', 'price', 'colors'];
const transforms = [unwind({ paths: ['colors'] })];
const json2csvParser = new Parser({ fields, transforms });
const csv = json2csvParser.parse(myCars);
console.log(csv);
will output to console
"carModel","price","colors"
"Audi",0,"blue"
"Audi",0,"green"
"Audi",0,"yellow"
"BMW",15000,"red"
"BMW",15000,"blue"
"Mercedes",20000,"yellow"
"Porsche",30000,"green"
"Porsche",30000,"teal"
"Porsche",30000,"aqua"
Example 8
You can also unwind arrays multiple times or with nested objects.
const { Parser, transforms: { unwind } } = require('json2csv');
const myCars = [
{
"carModel": "BMW",
"price": 15000,
"items": [
{
"name": "airbag",
"color": "white"
}, {
"name": "dashboard",
"color": "black"
}
]
}, {
"carModel": "Porsche",
"price": 30000,
"items": [
{
"name": "airbag",
"items": [
{
"position": "left",
"color": "white"
}, {
"position": "right",
"color": "gray"
}
]
}, {
"name": "dashboard",
"items": [
{
"position": "left",
"color": "gray"
}, {
"position": "right",
"color": "black"
}
]
}
]
}
];
const fields = ['carModel', 'price', 'items.name', 'items.color', 'items.items.position', 'items.items.color'];
const transforms = [unwind({ paths: ['items', 'items.items'] })];
const json2csvParser = new Parser({ fields, transforms });
const csv = json2csvParser.parse(myCars);
console.log(csv);
will output to console
"carModel","price","items.name","items.color","items.items.position","items.items.color"
"BMW",15000,"airbag","white",,
"BMW",15000,"dashboard","black",,
"Porsche",30000,"airbag",,"left","white"
"Porsche",30000,"airbag",,"right","gray"
"Porsche",30000,"dashboard",,"left","gray"
"Porsche",30000,"dashboard",,"right","black"
Example 9
You can also unwind arrays blanking the repeated fields.
const { Parser, transforms: { unwind } } = require('json2csv');
const myCars = [
{
"carModel": "BMW",
"price": 15000,
"items": [
{
"name": "airbag",
"color": "white"
}, {
"name": "dashboard",
"color": "black"
}
]
}, {
"carModel": "Porsche",
"price": 30000,
"items": [
{
"name": "airbag",
"items": [
{
"position": "left",
"color": "white"
}, {
"position": "right",
"color": "gray"
}
]
}, {
"name": "dashboard",
"items": [
{
"position": "left",
"color": "gray"
}, {
"position": "right",
"color": "black"
}
]
}
]
}
];
const fields = ['carModel', 'price', 'items.name', 'items.color', 'items.items.position', 'items.items.color'];
const transforms = [unwind({ paths: ['items', 'items.items'], blankOut: true })];
const json2csvParser = new Parser({ fields, transforms });
const csv = json2csvParser.parse(myCars);
console.log(csv);
will output to console
"carModel","price","items.name","items.color","items.items.position","items.items.color"
"BMW",15000,"airbag","white",,
,,"dashboard","black",,
"Porsche",30000,"airbag",,"left","white"
,,,,"right","gray"
,,"dashboard",,"left","gray"
,,,,"right","black"
Migrations
Migrating from 3.X to 4.X
What in 3.X used to be
const json2csv = require('json2csv');
const csv = json2csv({ data: myData, fields: myFields, unwindPath: paths, ... });
should be replaced by
const { Parser } = require('json2csv');
const json2csvParser = new Parser({ fields: myFields, unwind: paths, ... });
const csv = json2csvParser.parse(myData);
or the convenience method
const json2csv = require('json2csv');
const csv = json2csv.parse(myData, { fields: myFields, unwind: paths, ... });
Please note that many of the configuration parameters have been slightly renamed. Please check one by one that all your parameters are correct. You can se the documentation for json2csv 3.11.5 here.
Migrating from 4.X to 5.X
In the CLI, the config file option, -c, used to be a list of fields and now it's expected to be a full configuration object.
The stringify option hass been removed.
doubleQuote has been renamed to escapedQuote.
The unwind and flatten -related options has been moved to their own transforms.
What used to be
const { Parser } = require('json2csv');
const json2csvParser = new Parser({ unwind: paths, unwindBlank: true, flatten: true, flattenSeparator: '__' });
const csv = json2csvParser.parse(myData);
should be replaced by
const { Parser, transforms: { unwind, flatten } } = require('json2csv');
const json2csvParser = new Parser({ transforms: [unwind({ paths, blankOut: true }), flatten('__')] });
const csv = json2csvParser.parse(myData);
You can se the documentation for json2csv v4.X.X here.
Known Gotchas
Excel support
Avoiding excel autoformatting
Excel tries to automatically detect the format of every field (number, date, string, etc.) regardless of whether the field is quoted or not.
This might produce few undesired effects with, for example, serial numbers:
- Large numbers are displayed using scientific notation
- Leading zeros are stripped.
Enabling the excelString option produces an Excel-specific CSV file that forces Excel to interpret string fields as strings. Please note that the CSV will look incorrect if viewing it somewhere else than Excel.
Avoiding CSV injection
As part of Excel automatically format detection, fields regarded as formulas (starting with =, +, - or @) are interpreted regardless of whether the field is quoted or not, creating a security risk (see CSV Injection.
This issue has nothing to do with the CSV format, since CSV knows nothing about formulas, but with how Excel parses CSV files.
Enabling the excelString option produces an Excel-specific CSV file that forces Excel to interpret string fields as strings. Please note that the CSV will look incorrect if viewing it somewhere else than Excel.
Preserving new lines
Excel only recognizes \r\n as valid new line inside a cell.
Unicode Support
Excel can display Unicode correctly (just setting the withBOM option to true). However, Excel can't save unicode so, if you perform any changes to the CSV and save it from Excel, the Unicode characters will not be displayed correctly.
PowerShell escaping
PowerShell do some estrange double quote escaping escaping which results on each line of the CSV missing the first and last quote if outputting the result directly to stdout. Instead of that, it's advisable that you write the result directly to a file.
Building
json2csv is packaged using rollup. You can generate the packages running:
npm run build
which generates 3 files under the dist folder:
json2csv.umd.jsUMD module transpiled to ES5json2csv.esm.jsES5 module (import/export)json2csv.cjs.jsCommonJS module
When you use packaging tools like webpack and such, they know which version to use depending on your configuration.
Testing
Run the folowing command to check the code style.
$ npm run lint
Run the following command to run the tests and return coverage
$ npm run test-with-coverage
Contributors
After you clone the repository you just need to install the required packages for development by runnning following command under json2csv dir.
$ npm install
Before making any pull request please ensure sure that your code is formatted, test are passing and test coverage haven't decreased. (See Testing)
License
See LICENSE.md.