README
leylo 

| Installation | Requirements | Usage | Demo | 📚 API |
|---|
Asynchronous utility functions for Firestore within Vue CLI 3.
See a demo site here with source code here
▸ Installation
npm install leylo
If not using Firebase Hosting, there's no need to npm install firebase or npm install firebase-tools. Just plug in the credentials within your .env and you're good to go!
▸ Requirements
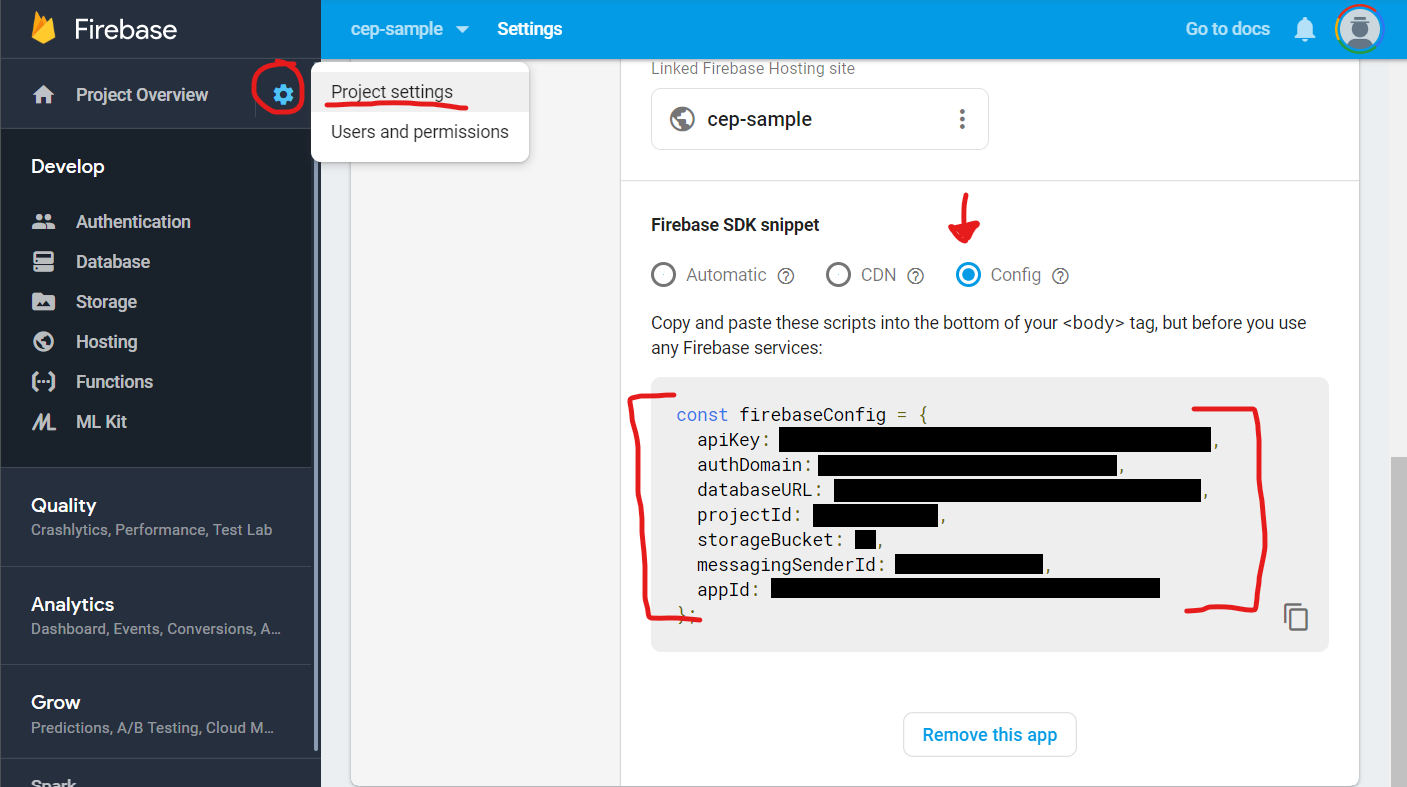
You must have a .env file at the root of your Vue CLI 3 repo containing the following key/value pairs (template available in this repo):
VUE_APP_FIREBASE_APIKEY=...
VUE_APP_FIREBASE_AUTHDOMAIN=...
VUE_APP_FIREBASE_DATABASEURL=...
VUE_APP_FIREBASE_PROJECTID=...
VUE_APP_FIREBASE_STORAGEBUCKET=...
VUE_APP_FIREBASE_MESSAGINGSENDERID=...
VUE_APP_FIREBASE_APPID=...
No quotation marks needed in .env values above
▸ Usage
<script>
// Within a .vue file
import leylo from "leylo";
export default {
name: "yourComponent",
// If using async/await, must define mounted/created/function as async
async mounted() {
let validation = await leylo.docExists("users", "Inventsable");
console.log(validation); // Returns true
// All functions are thenable if not using async
leylo.getDocById("users", "Inventsable").then(response => {
console.log(response); // Returns { name: 'Tom Scharstein', ... }
});
}
};
</script>
📚 API
All methods are accessible as properties of leylo, as in leylo.docExists(...).
📗 Global
📙 Retrieving Data
📘 Adding Data
📕 Deleting Data
◤ 📗 Global
◤ Click these arrows to return to the top of the API
.db
Returns Object of interior Firestore used for all queries.
console.log(leylo.db);
// Returns Firestore {_queue: AsyncQueue, INTERNAL: {…}, _config: FirestoreConfig, _databaseId: DatabaseId, _dataConverter: UserDataConverter, …}
Can be used as an alias to any custom Firestore query or method:
let query = leylo.db.collection("col");
query
.orderBy("foo")
.endAt(42)
.get()
.then(querySnapshot => {
querySnapshot.forEach(documentSnapshot => {
console.log(`Found document at ${documentSnapshot.ref.path}`);
});
});
◤ 📙 Retreiving Data
- leylo.docExists()
- leylo.collectionExists()
- leylo.getPath()
- leylo.getCollection()
- leylo.getDocById()
- leylo.getDocByField()
- leylo.getDocByQuery()
- leylo.getAllDocsByField()
- leylo.getAllDocsByQuery()
- leylo.getDocIdByField()
- leylo.getDocPathByField()
- leylo.streamCollection()
- leylo.streamPath()
- leylo.streamDocChangesById()
- leylo.streamDocChangesByField()
- leylo.streamDocChangesByQuery()
▲ .docExists(collection, id)
▲ Click these arrows to return to the top of each segment
Returns Boolean of whether document with specified id is found in Firestore
collection[String] - Name of collectionid[String] - Name/ID of document within collection
// WITHIN ASYNC FUNCTION
let validation = await leylo.docExists("users", "Inventsable");
console.log(validation); // Returns true
// OR THENABLE
leylo.docExists("users", "Inventsable").then(response => {
console.log(response); // Returns true
});
▲ .collectionExists(collection)
Returns Boolean of whether collection with specified name is found in Firestore
collection[String] - Name of collection
let validation = await leylo.collectionExists("users");
console.log(validation); // Returns true
▲ .getPath(path[, getData?])
Returns Array if collection, Object if document, or Any if field of specified path or False if not found
path[String] - Path in the form collection or collection/documentgetData[Boolean] (Default: true) - IftruereturnsdocumentSnapshot.data()else returnsdocumentSnapshot
// Simple grab all documents within a collection:
let userList = await leylo.getPath("users");
console.log(userList); // Returns [{…}, {…}, {…}, {…}, {…}]
// Simple grab single document from specific collection/document path:
let certainUser = await leylo.getPath("users/Inventsable");
console.log(userList); // Returns { name: 'Tom Scharstein', ... }
// Simple grab value from specific collection/document/field path:
let certainUserLocation = await leylo.getPath("users/Inventsable/location");
console.log(certainUserLocation); // Returns 'Arizona'
// Add all documents to a specified array in component's data
let doSomethingEveryUser = await leylo.getPath("users", false);
doSomethingEveryUser.forEach(user => {
this.userList.push(user.data());
});
// When adding to pre-existing array, add items which don't already exist in that array:
let addUsersAgain = await leylo.getPath("users");
addUsersAgain.forEach(user => {
// Add item to array if array doesn't contain this same key = value pair
// This is similar to Array.includes() and returns Boolean but by targeting Prop of Object within Array
if (!this.userList.some(person => person.fullName == user.fullName))
this.userList.push(user);
else console.log(`${user.fullName} already existed in this.userList`);
});
▲ .getCollection(collection[, getData?])
Returns Array of Objects within specified collection or False if not found
collection[String] - Name of collectiongetData[Boolean] (Default: true) - IftruereturnsdocumentSnapshot.data()else returnsdocumentSnapshot
// Simple grab all documents within a collection:
let userList = await leylo.getCollection("users");
console.log(userList); // Returns [{…}, {…}, {…}, {…}, {…}]
// If needing to grab the Document Reference, we can pass false to getData:
let doSomethingEveryUser = leylo.getCollection("users", false).then(users => {
users.forEach(user => {
console.log(`${user.id} is at ${user.ref.path} and contains:`); // Inventsable is at userList/Inventsable and contains
console.log(user.data()); // Returns Object with document contents { ... }
});
});
let doSomethingAsyncForList = await leylo.getCollection("users", false);
console.log("This prints at the top");
Promise.all(
doSomethingAsyncEveryUser.map(user => {
console.log(`This prints in the middle: ${user.id}`); // This prints in the middle: Inventsable
Promise.resolve(true);
})
);
console.log(`This prints at the bottom`);
// Now continue to next code
▲ .getDocById(collection, id[, getData?])
Returns Object with specified id in Firestore or False if not found
collection[String] - Name of collectionid[String] - Name/ID of document within collectiongetData[Boolean] (Default: true) - IftruereturnsdocumentSnapshot.data()else returnsdocumentSnapshot
let user = await leylo.getDocById("users", "Inventsable");
console.log(user); // Returns { name: 'Tom Scharstein', ... }
▲ .getDocByField(collection, field, value[, getData?])
Returns Object with specified field = value in Firestore or False if not found
collection[String] - Name of collectionfield[String] - Name of key/field of target documentvalue[String] - Value of key/field of target documentgetData[Boolean] (Default: true) - IftruereturnsdocumentSnapshot.data()else returnsdocumentSnapshot
let user = await leylo.getDocByField("users", "name", "Tom Scharstein");
console.log(user); // Returns { name: 'Tom Scharstein', ... }
▲ .getAllDocsByField(collection, field, value[, getData?])
Returns Array of every Object with specified field = value in collection or False if none found
collection[String] - Name of collectionfield[String] - Name of key/field of target documentvalue[String] - Value of key/field of target documentgetData[Boolean] (Default: true) - IftruereturnsdocumentSnapshot.data()else returnsdocumentSnapshot
let usersInArizona = await leylo.getAllDocsByField(
"users",
"location",
"Arizona"
);
// Returns [ {...}, {...}, {...} ]
usersInArizona.forEach(user => {
console.log(user); // Returns { name: 'Tom', location: 'Arizona', ... }
});
▲ .getDocIdByField(collection, field, value)
Same as using
await leylo.getDocByField("users", "name", "Tom Scharstein", false).id
Returns String of specified field = value document's id in collection or False if not found
collection[String] - Name of collectionfield[String] - Name of key/field of target documentvalue[String] - Value of key/field of target document
// If we don't know the path to our document, but know a certain key/value pair only it has:
let userId = await leylo.getDocIdByField("users", "name", "Tom Scharstein");
console.log(userId); // Returns 'Inventsable'
// We can query it to return the Document.id, and know the path must be users/Inventsable
let checkPath = await leylo.getPath("users/Inventsable");
console.log(checkPath); // Returns { name: 'Tom Scharstein', location: 'Arizona', ... }
▲ .getDocPathByField(collection, field, value)
Same as using
await leylo.getDocByField("users", "name", "Tom Scharstein", false).ref.path
Returns String with specified field = value document's path in Firestore or False if not found
collection[String] - Name of collectionfield[String] - Name of key/field of target documentvalue[String] - Value of key/field of target document
let fullPathToUser = await leylo.getDocPathByField(
"users",
"name",
"Tom Scharstein"
);
console.log(fullPathToUser); // Returns 'users/Inventsable'
▲ .getDocByQuery(collection, field, query, value[, getData?])
Returns first Object found with specified field (query) value in Firestore or False if not found
collection[String] - Name of collectionfield[String] - Name of key/field of target documentquery[String] - One of==,>=,<=,>,<,array_containsor valid Firebase query stringvalue[String] - Value of key/field of target documentgetData[Boolean] (Default: true) - IftruereturnsdocumentSnapshot.data()else returnsdocumentSnapshot
// Grab the first user containing key of temperature less than or equal to 10
let userInAlaska = await leylo.getDocByQuery("users", "temperature", "<=", 10);
console.log(userInAlaska); // Returns { name: 'John Doe' }
// Grab the first user where temperature is greator or equal to 10 as DocumentReference
let userNotInAlaska = await leylo.getDocByQuery(
"users",
"temperature",
">=",
10,
false // Passing false to getData gives us the DocumentReference
);
console.log(userNotInAlaska.ref.path); // Returns 'users/Inventsable'
▲ .getAllDocsByQuery(collection, field, query, value[, getData?])
Returns Array of every Object with specified field (query) value in Firestore or False if none found
collection[String] - Name of collectionfield[String] - Name of key/field of target documentquery[String] - One of==,>=,<=,>,<,array_containsor valid Firebase query stringvalue[String] - Value of key/field of target documentgetData[Boolean] (Default: true) - IftruereturnsdocumentSnapshot.data()else returnsdocumentSnapshot
// Get Array of all documents where temperature field contains value greater or equal to 110
let placeTooHotToLiveIn = await leylo.getAllDocsByQuery(
"states",
"temperature",
">="
110,
false
);
console.log(placesTooHotToLiveIn) // Returns [ {...}, {...}, {...} ]
placeTooHotToLiveIn.forEach(place => {
console.log(place); // Returns DocumentSnapshot{ ... }
});
▲ .streamCollection(collection[, callback, changeType, getData?])
Cannot be detached -- if needing programmatic detachment use .streamPath() instead
Returns every matching result of passing document Object as parameter to callback every time the collection is modified. Initial results are same as this.getCollection() but reactive and continuous to catch any docs added to this collection later and execute callback on them as well.
collection[String] - Name of collectioncallback[Function] (Default: null) - Function to execute on every change to document. Ifnull, returns directObjectaccording togetDataparameterchangeType[String] (Default: null) - Ifnulllisten to all, else one ofadded,modified, orremovedgetData[Boolean] (Default: true) - IftruepassesquerySnapshot.docChanges().data()tocallbackelse passesquerySnapshot.docChanges()
// Simple usage:
let streamUsers = await leylo.streamCollection("users", res => {
console.log("User detected:");
console.log(res); // Returns { name: 'Inventsable', ... }
});
// From the demo page:
let addUserStream = await leylo.streamCollection(
"users",
this.addUserIfNotInList,
"added"
);
// Above is the same as:
let addUserStream = await leylo.streamCollection(
"users",
user => {
// If this.userList doesn't already contain this user, add it to our component's data:
if (!this.userList.some(person => person.fullName == user.fullName))
this.userList.push(user);
},
"added"
);
// Automatically remove user from this.userList via method:
async mounted() {
this.startRemoveStream()
},
methods: {
async startRemoveStream() {
return await leylo.streamCollection(
"users",
user => {
// Easy to update by filtering this.userList to entries not equal to the document just removed:
this.userList = this.userList.filter(item => {
return item.fullName !== user.data().fullName;
});
},
"removed",
// Passing false to getData in case we need the Document.id or see changes
false
);
},
}
▲ .streamPath(path[, callback, changeType, getData?])
Returns Object which can be programmatically detached, but still executes callback on any document/data.
path[String] - Any valid path fromcollectiontocollection/documentcallback[Function] (Default: null) - Function to execute on every change to document. Ifnull, returns directObjectaccording togetDataparameterchangeType[String] (Default: null) - Ifnulllisten to all, else one ofadded,modified, orremovedgetData[Boolean] (Default: true) - IftruepassesquerySnapshot.docChanges().data()tocallbackelse passesquerySnapshot.docChanges()
async mounted() {
// Starts the stream
this.startStream();
// The method below results in a `Hello NAME` statement for any user added until the stream is detached.
setTimeout(() => {
// Stops streaming after 10 seconds.
this.stopStream()
}, 10000)
},
methods: {
async startStream() {
this.userStream = await leylo.streamPath(
"users",
user => {
this.greetingList.push(`Hello ${user.data().firstName}`);
},
"added",
false
);
},
async stopStream() {
// Firestore's detachment is odd. You have to call the stream as a function:
this.userStream();
}
}
▲ .streamDocChangesById(collection, id[, callback, changeType, getData?])
Returns result of passing document Object as parameter to callback every time the document is modified
collection[String] - Name of collectionid[String] - Name/ID of document within collectioncallback[Function] (Default: null) - Function to execute on every change to documentchangeType[String] (Default: null) - Ifnulllisten to all, else one ofadded,modified, orremovedgetData[Boolean] (Default: true) - IftruepassesquerySnapshot.docChanges().data()tocallbackelse passesquerySnapshot.docChanges()
// Can do this during created(), mounted() or some init function
let messages = await leylo.streamDocChangesById(
"messages",
"chatroomA",
newdata => {
// Executes every time a field is added, modified, or removed from this document
console.log("Document has changed to:");
console.log(newdata);
}
);
let userList = await leylo.streamDocChangesById(
"users",
"chatroomA",
this.addUser,
'added',
false
);
// Passing the data from above stream into one of our component's methods:
methods: {
addUser(doc) {
console.log(`New user was added at ${doc.ref.path} with contents:`)
console.log(doc.data())
}
}
▲ .streamDocChangesByField(collection, field, value[, callback, changeType, getData?])
Returns result of passing document Object as parameter to callback every time a document's field is modified
collection[String] - Name of collectionfield[String] - Name of key/field of target documentvalue[String] - Value of key/field of target documentcallback[Function] (Default: null) - Function to execute on every change to documentchangeType[String] (Default: null) - Ifnulllisten to all, else one ofadded,modified, orremovedgetData[Boolean] (Default: true) - IftruepassesquerySnapshot.docChanges().data()tocallbackelse passesquerySnapshot.docChanges()
let usersCurrentlyInArizona = await leylo.streamDocChangesByField(
"users",
"location",
"Arizona"(doc => {
console.log(`${doc.ref.path} is now in Arizona`);
}),
"modified",
false
);
▲ .streamDocChangesByQuery(collection, field, query, value[, callback, changeType, getData?])
Returns every matching result of passing document Object as parameter to callback every time the document is modified
collection[String] - Name of collectionfield[String] - Name of key/field of target documentquery[String] - One of==,>=,<=,>,<,array_containsor valid Firebase query stringvalue[String] - Value of key/field of target documentcallback[Function] (Default: null) - Function to execute on every change to documentchangeType[String] (Default: null) - Ifnulllisten to all, else one ofadded,modified, orremovedgetData[Boolean] (Default: true) - IftruepassesquerySnapshot.docChanges().data()tocallbackelse passesquerySnapshot.docChanges()
let usersLeavingArizona = await leylo.streamDocChangesByField(
"users",
"temperature",
"<=",
110,
doc => {
console.log(`${doc.ref.path} has left Arizona`);
},
"modified",
false
);
◤ 📘 Adding Data
- leylo.addDoc()
- leylo.addAllDocs()
- leylo.setPath()
- leylo.setDocByPath()
- leylo.setAllDocsByPath()
- leylo.setDocById()
- leylo.setAllDocsById()
- leylo.setFieldByPath()
- leylo.setFieldById()
▲ .addDoc(collection, data)
Returns DocumentReference result of writing new document with auto-generated id to collection
collection[String] - Name of collectiondata[Object] - Contents of document to write
let user = await leylo.addDoc("users", {
name: "Random",
location: "Random"
});
console.log(user); // Returns DocumentSnapshot{ ... }
console.log(user.id); // Returns 'cmeJ6JeoTCIfvMvgE2ru', auto-generated id
console.log(user.ref.path); // Returns 'users/cmeJ6JeoTCIfvMvgE2ru'
console.log(user.data()); // Returns { name: 'Random', location: 'Random' }
▲ .addAllDocs(collection, ...docs)
Returns Array of DocumentReferences of newly written documents to collection
collection[String] - Name of collectiondocs[Array] - Array containingObjects to be written as documents (without ids)
let newUsers = await leylo.addAllDocs(
"users",
...[{ name: "SomeGuy" }, { name: "SomeGirl" }]
);
console.log(docsCreatedWithGeneratedIds); // Returns [DocumentReference, DocumentReference]
▲ .setPath(path, data[, overwrite?])
Shorthand method for writing document or field, will parse
pathand redirect to either leylo.addDoc(), leylo.addDocById(), or leylo.setFieldByPath()
Returns Boolean of whether the document/field was successfully written or Object DocumentReference if path was only a collection
path[String] - Path in the form collection/documentdata[Any] - Contents of document to write or append. If writing document, should beObject, but if field can be anything (except forArraywithinArrayper Firestore limitation)overwrite[Boolean] (Default: false) - Iffalse, merge newdatawith pre-existing document or overwrite if it already exists, but iftruereplace document entirely with newdata
// Can be used to create new document or merge/add field into pre-existing document
let setLocation = await leylo.setPath("users/Inventsable", {
location: "Colorado"
});
console.log(setLocation); // Returns true
// If location already existed, rewrite it's contents to the new value:
let newUser = await leylo.setPath("users", {
name: "John Doe",
location: "Washington"
});
console.log(newUser); // Returns DocumentReference{ ... }
// Rewrite individual field:
let rewriteUserData = await leylo.setPath(
"users/Inventsable/location",
"Arizona"
);
console.log(rewriteUserData); // Returns true
▲ .setDocByPath(path, data[, overwrite?])
Unlike leylo.setPath(), this method will return an Error if path points to collection or field.
Returns Boolean of whether the document was successfully written to collection
path[String] - Path in the form collection/documentdata[Object] - Contents of document to write or appendoverwrite[Boolean] (Default: false) - Iffalse, merge newdatawith pre-existing document or overwrite if it already exists, but iftruereplace document entirely with newdata
// If user 'Inventsable' already has content but no location, merge it as a new field:
let setLocation = await leylo.setDocByPath("users/Inventsable", {
location: "Colorado"
});
console.log(setLocation); // Returns true
// If location already existed, rewrite it's contents to the new value:
let rewriteLocation = await leylo.setDocByPath("users/Inventsable", {
location: "Washington"
});
console.log(rewriteLocation); // Returns true
// If overwrite is true, replace document at path entirely:
let rewriteUserData = await leylo.setDocByPath(
"users/Inventsable",
{
name: "Tom Scharstein",
location: "Tempe",
status: "Working"
},
true
);
console.log(rewriteUserData); // Returns true
▲ .setAllDocsByPath(overwrite, ...docs)
Returns Array of Booleans the length of docs array for whether document was successfully written to Firestore
data[Object] - Contents of document to write or appendoverwrite[Boolean] (Default: false) - Iffalse, merge newdatawith pre-existing document or overwrite if it already exists, but iftruereplace document entirely with newdata
// Each data is an array in the form [ 'path', contents]
let users = [
["users/Inventsable", { name: "Tom" }],
["users/somePerson", { name: "John" }],
["users/someOtherPerson", { name: "Jane" }]
];
let writeUsers = await leylo.setAllDocsByPath(true, ...users);
console.log(writeUsers); // Returns [true, true, true]
let newLocations = [
["users/Inventsable", { location: "Arizona" }],
["users/somePerson", { location: "Arizona" }],
["users/someOtherPerson", { location: "Arizona" }]
];
let mergeNewLocations = await leylo.setAllDocsByPath(false, ...newLocations);
console.log(writeUsers); // Returns [true, true, true]
▲ .setDocById(collection, id, data[, overwrite?])
Returns Boolean of whether the document was successfully written to collection
collection[String] - Name of collectionid[String] - Name/ID of document within collectiondata[Object] - Contents of document to writeoverwrite[Boolean] (Default: false) - Iffalse, merge newdatawith pre-existing document, but iftruereplace document entirely with newdata
let setAnotherLocation = await leylo.setDocById(
"users",
"Inventsable",
{ location: "Colorado" },
false
);
console.log(setAnotherLocation);
▲ .setAllDocsById(collection, overwrite, ...docs)
Returns Array of Booleans the length of docs array for whether document was successfully written to Firestore
collection[String] - Name of collectionoverwrite[Boolean] (Default: false) - Iffalse, merge newdatawith pre-existing document, but iftruereplace document entirely with newdatadocs[Array] - Contents of document to write as[ 'id', contents ]
// Each document is an array in the form [ 'id', contents]
let users = [
["Inventsable", { name: "Tom" }],
["SomeNameHere", { name: "John" }],
["ScreenName", { name: "Jane" }]
];
let writeUsers = await leylo.setAllDocsById("users", true, ...users);
console.log(writeUsers); // Returns [true, true, true]
▲ .setFieldByPath(path, value)
Returns Boolean of whether the field was successfully written to path
path[String] - Path in the form collection/document/fieldvalue[Any] - New value to write to specifiedpath
let updateUserLocation = await leylo.setFieldByPath(
"users/Inventsable/location",
"Alaska"
);
console.log(updateUserLocation); // Returns true
▲ .setFieldById(collection, id, field, value)
Returns Boolean of whether the field was successfully written to path
collection[String] - Name of collectionid[String] - Name/ID of document within collectionfield[String] - Name of key within documentvalue[Any] - New value to write to specifiedpath
let setNewLocation = await leylo.setFieldByDocId(
"users",
"Inventsable",
"location",
"Colorado"
);
console.log(setNewLocation);
◤ 📕 Deleting Data
- leylo.deletePath()
- leylo.deleteCollection()
- leylo.deleteDocById()
- leylo.deleteAllDocsByField()
- leylo.deleteAllDocsByQuery()
- leylo.deleteFieldByDocId()
- leylo.deleteAllFieldsContainingValue()
- leylo.deleteAllFieldsByQuery()
▲ .deletePath(path)
NOTE: If deleting a collection which has a stream, the stream is automatically detached.
Returns Boolean if path was successfully deleted
path[String] - Any valid path fromcollectiontocollection/document/field
let deleteCertainUser = await leylo.deletePath("users/Inventsable");
if (deleteCertainUser) console.log("I was deleted!");
// Delete entire collection:
leylo.deletePath("users").then(result => {
console.log(result); // Returns true
});
▲ .deleteCollection(collection)
Same as using
await leylo.deletePath(collection)
Returns Array of Booleans for number of documents successfully deleted
collection[String] - Name of collection
// Delete entire collection:
leylo.deleteCollection("users").then(result => {
console.log(result); // Returns true
});
let fullDeletion = await leylo.deleteCollection("users");
console.log(fullDeletion); // Returns false because collection doesn't exist, was deleted above
▲ .deleteDocById(collection, id)
Returns Boolean
collection[String] - Name of collectionid[String] - Name/ID of document within collection
let deleteCertainUser = await leylo.deletePath("users", "Inventsable");
console.log(deleteCertainUser); // Returns true
▲ .deleteAllDocsByField(collection, field, value)
Returns Array of Booleans for whether documents were successfully deleted
collection[String] - Name of collectionfield[String] - Name of key within documentvalue[Any] - New value to write to specifiedpath
let deleteAllArizonaResidents = await leylo.deleteAllDocsByField(
"users",
"location",
"Arizona"
);
console.log(deleteAllArizonaResidents); // Returns [ true, true, true ]
deleteAllArizonaResidents.forEach(status => {
console.log(status); // Returns true
});
▲ .deleteAllDocsByQuery(collection, field, query, value)
Returns Array of Booleans for whether docs were successfully deleted
collection[String] - Name of collectionfield[String] - Name of key within documentquery[String] - One of==,>=,<=,>,<,array_containsor valid Firebase query stringvalue[Any] - New value to write to specifiedpath
let deleteAllArizonaResidents = await leylo.deleteAllDocsByQuery(
"users",
"temperature",
">=",
110
);
console.log(deleteAllArizonaResidents); // Returns [ true, true, true ]
deleteAllArizonaResidents.forEach(status => {
console.log(status); // Returns true
});
▲ .deleteFieldByDocId(collection, id, field)
Returns Boolean for whether field was successfully deleted from document
collection[String] - Name of collectionid[String] - Name/ID of document within collectionfield[String] - Name of key within document
let deleteLocation = await leylo.deleteFieldByDocId(
"users",
"Inventsable",
"location"
);
console.log(deleteLocation); // Returns true
▲ .deleteAllFieldsContainingValue(collection, field, value)
Returns Array of Booleans for whether fields were successfully deleted
collection[String] - Name of collectionfield[String] - Name of key within documentvalue[Any] - New value to write to specifiedpath
let deleteAllArizonaLocations = await leylo.deleteAllFieldsContainingValue(
"users",
"location",
"Arizona"
);
console.log(deleteAllArizonaResidents); // Returns [ true, true, true ]
deleteAllArizonaResidents.forEach(status => {
console.log(status); // Returns true
});
// Unlike leylo.deleteAllDocsByQuery() or like, this only deletes the field 'location' instead of entire doc.
▲ .deleteAllFieldsByQuery(collection, field, query, value)
Returns Array of Booleans for whether fields were successfully deleted
collection[String] - Name of collectionfield[String] - Name of key within documentquery[String] - One of==,>=,<=,>,<,array_containsor valid Firebase query stringvalue[Any] - New value to write to specifiedpath
let deleteAllArizonaLocations = await leylo.deleteAllFieldsContainingValue(
"users",
"location",
"==",
"Arizona"
);
console.log(deleteAllArizonaLocations); // Returns [ true, true, true ]
deleteAllArizonaLocations.forEach(status => {
console.log(status); // Returns true
});
let deleteAllAlaskaLocations = await leylo.deleteAllFieldsContainingValue(
"users",
"temperature",
"<=",
10
);
console.log(deleteAllAlaskaLocations); // Returns [ true, true, true ]
deleteAllAlaskaLocations.forEach(status => {
console.log(status); // Returns true
});
