README
playwright-fluent
Fluent API around Playwright
Fluent API | Selector API | Assertion API | Mock API | FAQ | with jest | with cucumber-js v6 | with cucumber-js v7
Installation
npm i --save playwright-fluent
If not already installed, the playwright package should also be installed with a version >= 1.12.0
Usage
import { PlaywrightFluent, userDownloadsDirectory } from 'playwright-fluent';
const p = new PlaywrightFluent();
await p
.withBrowser('chromium')
.withOptions({ headless: false })
.withCursor()
.withDialogs()
.recordPageErrors()
.recordFailedRequests()
.recordDownloadsTo(userDownloadsDirectory)
.emulateDevice('iPhone 6 landscape')
.navigateTo('https://reactstrap.github.io/components/form/')
.click('#exampleEmail')
.typeText('foo.bar@baz.com')
.pressKey('Tab')
.expectThatSelector('#examplePassword')
.hasFocus()
.typeText("don't tell!")
.pressKey('Tab')
.expectThatSelector('#examplePassword')
.hasClass('is-valid')
.hover('#exampleCustomSelect')
.select('Value 3')
.in('#exampleCustomSelect')
.close();
This package provides also a Selector API that enables to find and target a DOM element or a collection of DOM elements embedded in complex DOM Hierarchy:
const selector = p
.selector('[role="row"]') // will get all dom elements, within the current page, with the attribute role="row"
.withText('foobar') // will filter only those that contain the text 'foobar'
.find('td') // from previous result(s), find all embedded <td> elements
.nth(2); // take only the second cell
await p.expectThatSelector(selector).hasText('foobar-2');
Usage with Iframes
This fluent API enables to seamlessly navigate inside an iframe and switch back to the page:
const p = new PlaywrightFluent();
const selector = 'iframe';
const inputInIframe = '#input-inside-iframe';
const inputInMainPage = '#input-in-main-page';
await p
.withBrowser('chromium')
.withOptions({ headless: false })
.withCursor()
.navigateTo(url)
.hover(selector)
.switchToIframe(selector)
.click(inputInIframe)
.typeText('hey I am in the iframe')
.switchBackToPage()
.click(inputInMainPage)
.typeText('hey I am back in the page!');
Usage with Dialogs
This fluent API enables to handle alert, prompt and confirm dialogs:
const p = new PlaywrightFluent();
await p
.withBrowser(browser)
.withOptions({ headless: true })
.WithDialogs()
.navigateTo(url)
// do some stuff that will open a dialog
.waitForDialog()
.expectThatDialog()
.isOfType('prompt')
.expectThatDialog()
.hasMessage('Please say yes or no')
.expectThatDialog()
.hasValue('yes')
.typeTextInDialogAndSubmit('foobar');
Usage with the tracing API
This fluent API enables to handle the playwright tracing API in the following way:
const p = new PlaywrightFluent();
await p
.withBrowser(browser)
.withOptions({ headless: true })
.withTracing()
.withCursor()
.startTracing({ title: 'my first trace' })
.navigateTo(url)
// do some stuff on the opened page
.stopTracingAndSaveTrace({ path: path.join(__dirname, 'trace1.zip') })
// do other stuff
.startTracing({ title: 'my second trace' })
// do other stuff
.stopTracingAndSaveTrace({ path: path.join(__dirname, 'trace2.zip') });
Usage with collection of elements
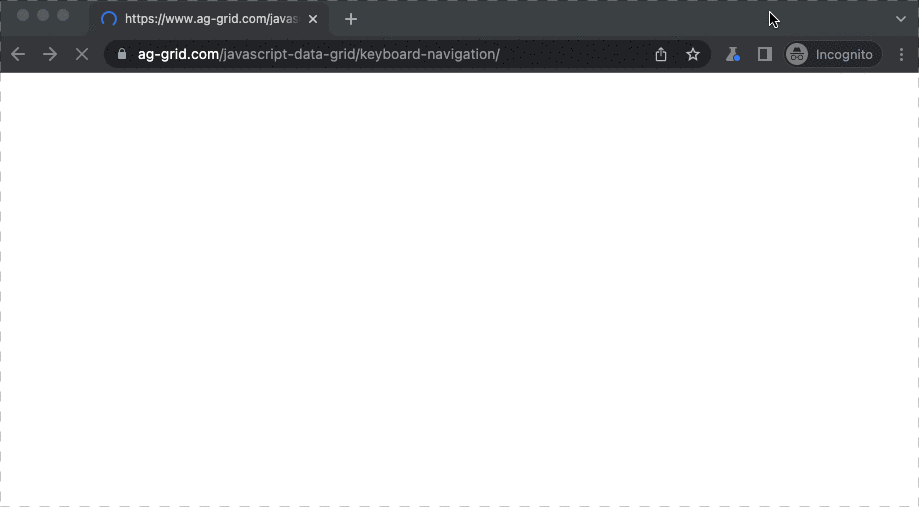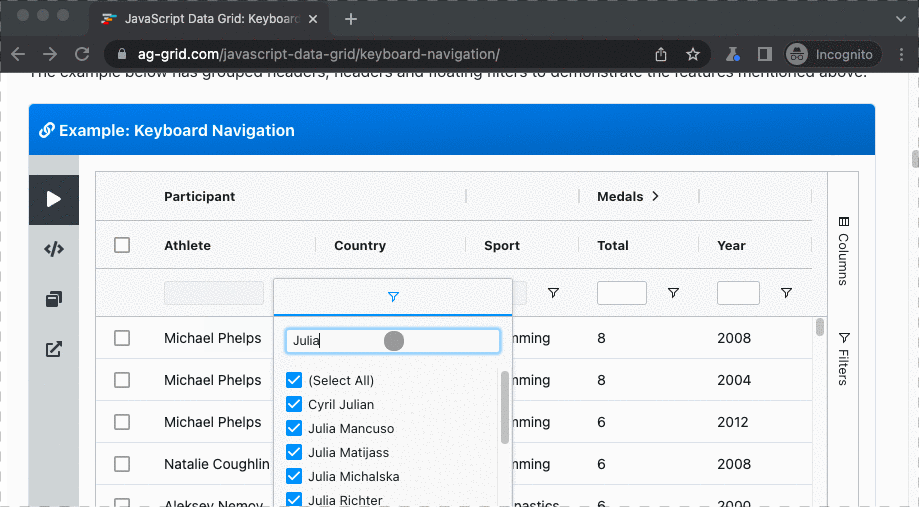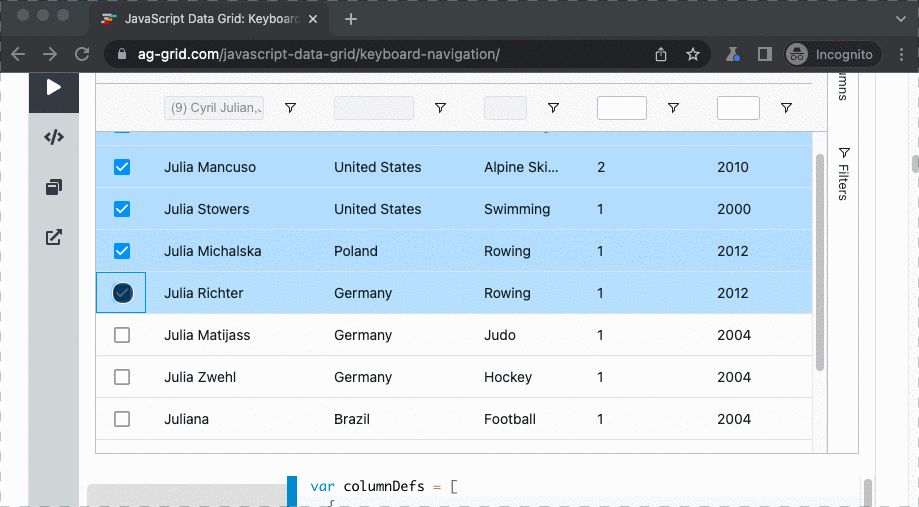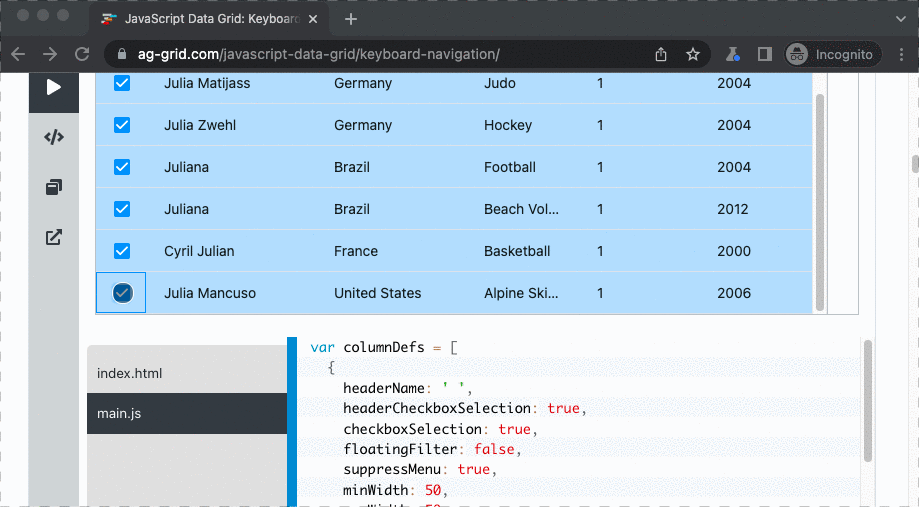
This fluent API enables to perform actions and assertions on a collection of DOM elements with a forEach() operator.
See it below in action on ag-grid where all athletes with Julia in their name must be selected:
const p = new PlaywrightFluent();
const url = `https://www.ag-grid.com/javascript-data-grid/keyboard-navigation/`;
const cookiesConsentButton = p
.selector('#onetrust-button-group')
.find('button')
.withText('Accept All Cookies');
const gridContainer = 'div#myGrid';
const rowsContainer = 'div.ag-body-viewport div.ag-center-cols-container';
const rows = p.selector(gridContainer).find(rowsContainer).find('div[role="row"]');
const filter = p.selector(gridContainer).find('input[aria-label="Athlete Filter Input"]').parent();
await p
.withBrowser('chromium')
.withOptions({ headless: false })
.withCursor()
.navigateTo(url)
.click(cookiesConsentButton)
.switchToIframe('iframe[title="grid-keyboard-navigation"]')
.hover(gridContainer)
.click(filter)
.typeText('Julia')
.pressKey('Enter')
.expectThat(rows.nth(1))
.hasText('Julia');
await rows.forEach(async (row) => {
const checkbox = row
.find('input[aria-label="Press Space to toggle row selection (unchecked)"]')
.parent();
await p.click(checkbox);
});
Usage with Stories
This package provides a way to write tests as functional components called Story:
stories.ts
import { Story, StoryWithProps } from 'playwright-fluent';
export interface StartAppProps {
browser: BrowserName;
isHeadless: boolean;
url: string;
}
// first story: start the App
export const startApp: StoryWithProps<StartAppProps> = async (p, props) => {
await p
.withBrowser(props.browser)
.withOptions({ headless: props.isHeadless })
.withCursor()
.navigateTo(props.url);
}
// second story: fill in the form
export const fillForm: Story = async (p) => {
await p
.click(selector)
.select(option)
.in(customSelect)
...;
};
// threrd story: submit form
export const submitForm: Story = async (p) => {
await p
.click(selector);
};
// fourth story: assert
export const elementIsVisible: Story = async (p) => {
await p
.expectThatSelector(selector)
.isVisible();
};
test.ts
import { startApp, fillForm } from 'stories';
import { PlaywrightFluent } from 'playwright-fluent';
const p = new PlaywrightFluent();
await p
.runStory(startApp, { browser: 'chrome', isHeadless: false, url: 'http://example.com' })
.runStory(fillForm)
.close();
// Also methods synonyms are available to achieve better readability
const user = new PlaywrightFluent();
await user
.do(startApp, { browser: 'chrome', isHeadless: false, url: 'http://example.com' })
.and(fillForm)
.attemptsTo(submitForm)
.verifyIf(elementIsVisible)
.close();
Usage with mocks
This fluent API provides a generic and simple infrastructure for massive request interception and response mocking.
This Mock API leverages the Playwright request interception infrastructure and will enable you to mock all HTTP requests in order to test the front in complete isolation from the backend.
Read more about the Fluent Mock API
This API is still a draft and is in early development, but stay tuned!
Contributing
Check out our contributing guide.
Resources
- Playwright Fluent API documentation
- Selector API documentation
- Assertion API documentation
- Mock API documentation
FAQ
Q: How does playwright-fluent relate to Playwright?
playwright-fluent is just a wrapper around the Playwright API.
It leverages the power of Playwright by giving a Fluent API, that enables to consume the Playwright API with chainable actions and assertions.
The purpose of playwright-fluent is to be able to write e2e tests in a way that makes tests more readable, reusable and maintainable.
Q: Can I start using playwright-fluent in my existing code base?
Yes you can.
import { PlaywrightFluent } from 'playwright-fluent';
// just create a new instance with playwright's browser and page instances
const p = new PlaywrightFluent(browser, page);
// you can also create a new instance with playwright's browser and frame instances
const p = new PlaywrightFluent(browser, frame);
// now you can use the fluent API
Q: Can I use Playwright together with the playwright-fluent?
Yes you can. To use the Playwright API, call the currentBrowser() and/or currentPage() methods exposed by the fluent API:
const browser = 'chromium';
const p = new PlaywrightFluent();
await p
.withBrowser(browser)
.emulateDevice('iPhone 6 landscape')
.withCursor()
.navigateTo('https://reactstrap.github.io/components/form/')
...;
// now if you want to use the playwright API from this point:
const browser = p.currentBrowser();
const page = p.currentPage();
// the browser and page objects are standard playwright objects
// so now you are ready to go by using the playwright API
Q: What can I do with the currently published npm package playwright-fluent?
The documentations:
- Playwright Fluent API documentation
- Selector API documentation
- Assertion API documentation
- Mock API documentation
reflect the current status of the development and are inline with the published package.
Q: Do you have some samples on how to use this library?
Yes, have a look to this demo project with jest, this demo project with cucumber-js v6 or this demo project with cucumber-js v7.
