README
react-three-resize-helper
A React hook for responsive design with three.js and react-three-fiber.
with useResizeHelper, you can easily use canvas aspect breakpoints and add changes to your three.js scene that will automatically apply at those breakpoints.
Make your scene adjustments based on position and size data provided by useResizeHelper.
Motivation
3D scenes and apps like games are often built for a set aspect ratio. When it comes to integrating 3D designs in regular websites, it becomes much more likely for the canvas to take on different aspect ratios, e.g. if the canvas is fixed to the viewport dimensions.
If a scene is only designed for a single aspect ratio, 3D elements in the scene could be cut off, sized in an undesirable way, or be positioned poorly when the aspect changes.
Just like in regular responsive web design, the goal in responsive 3D design is to always position the objects in the scene correctly in the camera's view. In HTML and CSS, we use width and height breakpoints. In a 3D scene, aspect breakpoints are a better choice.
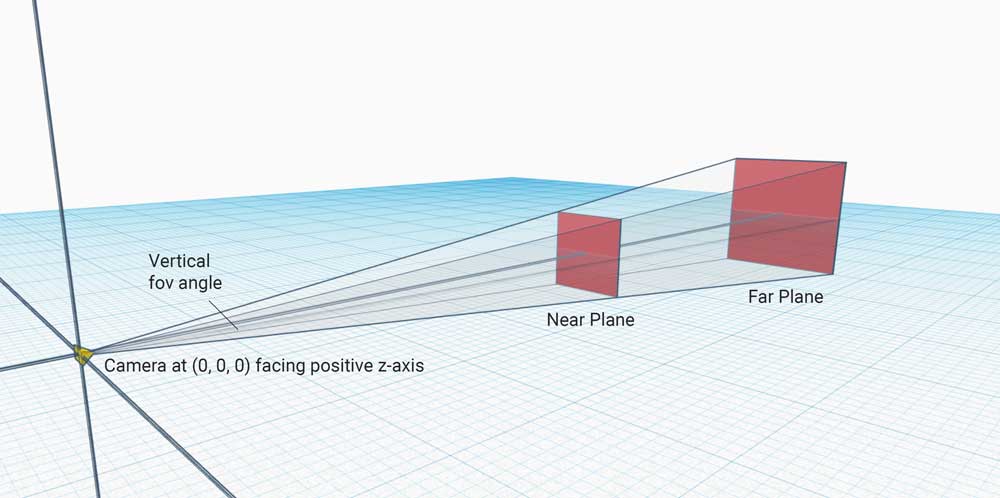
Because the three.js camera is defined with a vertical fov, the scene will always show the same thing in the vertical axis. This is different from traditional design with markdown and stylesheets that is based on vertical overflows and scroll.
For this reason, aspect breakpoints are better suited for these purposes.
See here for background information.
What is this hook?
This hook provides a way to easily make changes to your scene when the aspect ratio of the camera changes. It also returns some useful size and position data.
Changes to the canvas size will cause a re-render as the hook will run again and update your scene.
You can use a hook for each object you need to change, enabling you to encapsulate the design into the component like you would with CSS-in-JS.
Example:
const myThreeComponent = () => {
const options = {breakpoints: [1], positions: [[0, 0, 0], [10, 10, 10]];}
const ref = React.usRef();
useResizeHelper(ref, camera, options);
return <threeComponent ref={ref} />;
};
The snippet above defines a max-aspect breakpoint like a css max-width breakpoint. There are two ranges defined by it: aspects equal to or less 1, and aspects greater than 1. At the former aspect range, the hook sets the 3D objects's position to (0, 0, 0). At the latter range, the hook sets the object's position to (10, 10, 10);
Does this code look funny? Check out react-three-fiber.
Requirements
Please ensure that your camera's world direction is
(0, 0, 1), i.e., it should point toward the world's z-axis. If the camera and world have the same coordinate system, there is no need for projection calculations in the x and y direction. You can translate your camera along the z-axis with no issue, i.e. your camera's position(0, 0, z)can take any value for z.Your camera aspect must already respond to canvas element size changes.
react-three-fibersets this up out of the box.
Getting Started
Install:
npm i react-three-resize-helper
Install the peer dependency, which you'll need ayway:
npm i three
Import the hook:
import { useResizeHelper } from "react-three-resize-helper";
Usage
If you don't need to use aspect breakpoints
You can declaratively set properties of your 3D objects, especially if you use a three.js React component framework like react-three-fiber.
const myThreeComponent = () => {
const ref = React.usRef();
const data = useResizeHelper(ref, camera);
/* in this case, z = 10 */
return (
<threeComponent
ref={ref}
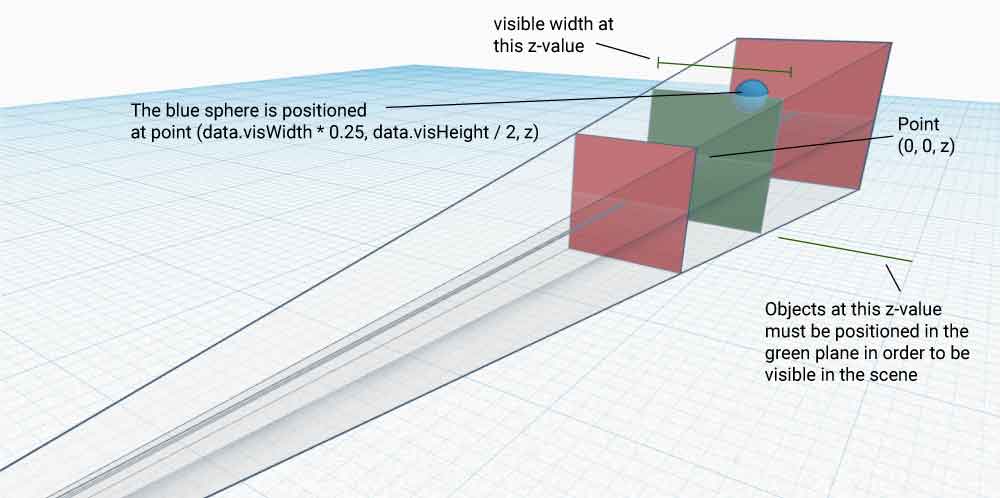
position={[data.visWidth * 0.25, data.visHeight / 2, 10]
/>
);
};
The object above will always be placed three quarters to the left of the screen and aligned at the top of the canvas.
Repsonsively changing the scene to different aspect ratios
You can use the hook to change objects of the scene at different aspect ratio breakpoints.
const myThreeComponent = () => {
const ref = React.usRef();
const otherRef = React.useRef();
const options = {
breakpoints: [0.474, 0.778],
positions: [
[
(info, scope) => [
scope.otherRef.position.x + 5,
scope.otherRef.position.y,
scope.otherRef.position.z,
],
],
[
(info, scope) => [
scope.otherRef.position.x + 3,
scope.otherRef.position.y,
scope.otherRef.position.z,
],
],
[
(info, scope) => [
scope.otherRef.position.x + 1,
scope.otherRef.position.y,
scope.otherRef.position.z,
],
],
],
functionScope: { otherRef },
useMin: true,
};
useResizeHelper(ref, camera, options);
return (
<>
<react3FiberComponent ref={ref} />
<react3FiberComponent ref={otherRef} />
</>
);
};
The snippet above positions one object in the scene relative to another object's position. It uses useResizeHelper to declare two aspect breakpoints. Using useMin: true tells the hook these are minimum aspect breakpoints, like CSS min-width breakpoints.
The breakpoints array of length n defines n + 1 aspect ranges. In this case, there are three ranges: aspects below 0.474, aspects equal to or above 0.474, and aspects equal to or above 0.778. Whatever changes we put in the positions object will be applied at these three ranges, respectively.
If we were to use maximum aspect breakpoints in the snippet above, the ranges to apply the changes would be for aspects equal to 0.474 or lower, aspects above 0.474 but lower than 0.778, and for aspects above 0.778.
Note: unlike with CSS, there is no cascading of styles. You should explicitly set your changes for each range depending on your breakpoints and whether useMin is true or false.
In the snippet above, the callback for the current aspect calculates the required position and returns a point in the form of an array containing the x, y, and z values, respectively. It uses a reference to another object because it is calculating position for one object based on another object's position.
Instead of a callback, we could have entered an array with some value or expression for each of the axes:
positions: [
[0, 0, 5],
[0, 0, 3],
[0, 0, 1],
],
API
useResizeHelper(ref, camera, options)
Return value
A regular object with the following properties:
- aspect: Number
The aspect ratio of the provided three.js camera. The hook updates when the aspect changes, e.g. when the canvas size changes.
- objMin: THREE.Vector3, objMax: THREE.Vector3
The minimum and maximum positional values of the bounding box of the object at ref.current in all three dimensions.
No different than:
new THREE.Box3().setFromObject(ref.current).min;
and
new THREE.Box3().setFromObject(ref.current).max;
- visWidth: Number, visHeight: Number
The width and height, in three.js world units, of the visible plane at the object's position relative to the camera.
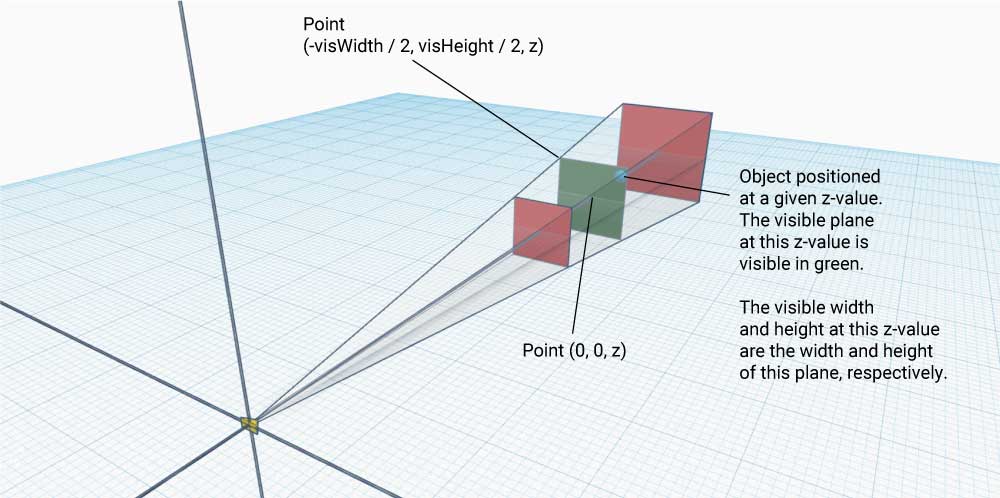
The center will always be at point (0, 0) provided that the camera is positioned as required above.
(-visWidth / 2, - visHeight / 2, z), for example, is at the bottom left corner of the canvas.
Parameters
- ref | React Ref | Required
A ref to an Object3D or other three.js 3D component. useResizeHelper uses this object's z-coordinate to calculate the visible width and height at the object's position. These numbers are returned by the hook. You can use properties in options to change properties of this object responsivley.
- camera | THREE.PerspectiveCamera | Required
A reference to the three.js perspective camera that your scene uses.
- options | Object | Optional
An object containing the following properties:
breakpoints | Array | Required
An array of Numbers specifying the breakpoints at which changes should apply. For example, [0.5, 1] specifies three distinct aspect ratio ranges, depending on the value of useMin.
If useMin is true, you should specify changes for the following aspect ranges:
[0, 0.5)[0.5, 1)[1, Infinity)
If useMin is false, you should specify changes for the following aspect ranges:
[0, 0.5](0.5, 1](1, Infinity)
useMin | Boolean | Optional (Default: false)
A Boolean that determines whether the defined breakpoints are minimum-aspect breakpoints (useMin is true) or maximum-aspect breakpoints (useMin is false -- the default);
See the breakpoints description to see an example of how useMin can change the aspect point ranges.
functionScope | Object | Optional
An object containing properties to which you need access in your callback functions. All callback functions can take two parameters:
const callback = (info, scope) => {};
info is the same object returned by useResizeHelper. scope is the object defined here.
setFunc | Array | Optional
An array of functions whose length is the same as breakpoints.length + 1. It defines callback functions to be run at each aspect range. The functions can use the parameters info, the same object that is returned from useResizeHelper, and scope, the object defined in functionScope:
(info, scope) => {
//your changes here
};
If null, no function will be called at this aspect range.
NOTE: functions of setFunc run after the changes made by the convenience properties positions, rotations, scales, fovs, and camZs.
Example usage:
const options = {
functionScope: { ref },
breakpoints: [0, 1],
setFunc: [
() => {
camera.position.z = 0;
camera.position.x = 0;
},
(info, scope) => {
camera.position.x = -info.visWidth / 2;
scope.ref.current.position.x = 0;
},
null,
],
};
positions | Array | Optional
A convenience property. An array containing the positional changes to be made to the object at ref.current at the specified breakpoints. The length of this array should be greater than the breakpoints array by a value of one, since n breakpoints specify n + 1 aspect ranges.
The members of this array can be one of the following:
- An array of x-, y-, and z-coordinate positional values to be applied to the object at
ref.current.
For example, [0.5, 2, 1] would change the position of the object to (0.5, 2, 1) at the aspect range it is specified for. It is no different than the following snippet:
ref.current.position.x = 0.5;
ref.current.position.y = 0.2;
ref.current.position.z = 1;
You can use null in any of the coordinates if you don't wish to make any changes to it at that breakpoint.
A function
(info, scope) => [x, y, z]returning an array like the one described above. The function takes two parameters:info, an object with the same properties as those returned byuseResizeHelper, andscope, the object optionally defined insetFunc(see above for more info).null, if no positional changes should be made at this breakpoint.
Example usage:
const options = {
breakpoints: [0.5, 1],
positions: [[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], (info) => [info.visWidth * 0.25, 0, 0]],
useMin: true,
};
Since useMin is true, the above snippet will place the object at the point (0, 0, 0) at the aspect range [0, 1) and at the point (info.visWidth * 0.25, 0, 0) at the aspect range [1, Infinity).
rotations | Array | Optional
The same as positions but instead of positional changes, it specifies rotational changes.
Note: the units for positional rotations are radians.
scales | Array | Optional
The same as positions but instead of positional changes, it specifies scale factors for each axis.
fovs | Array | Optional
The same as positions but instead of positional changes, it specifies camera fov at each breakpoint.
Since the fov is one Number, the members of this array can either be a Number or a function returning a Number.
Example usage:
const options = {
breakpoints: [0.5, 1],
fovs: [50, 60, (info) => (info.visWidth > 20 ? 60 : 50)],
useMin: true,
};
camZs | Array | Optional
The same as fovs but instead of fov value changes, it specifies changes to camera position along the axis (since the camera is required to be at (0, 0, z).
Test Server CLI
Coming soon.

